Uninstall Rust: The Definitive Guide for 2024
Frustrated with Rust taking up space or encountering issues? This comprehensive guide provides everything you need to know to uninstall Rust completely and correctly from your system. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned developer, we’ll walk you through each step, ensuring a clean removal and preventing potential problems down the line. This isn’t just a quick uninstall guide; it’s a deep dive into the process, offering expert insights and troubleshooting tips based on our extensive experience. You’ll gain a clear understanding of the different uninstall methods, how to handle common errors, and what to do if you encounter persistent files.
We’ve compiled this guide to be the most thorough and trustworthy resource available, reflecting our commitment to providing accurate, up-to-date, and helpful information. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and tools to confidently uninstall Rust and reclaim your system resources. Let’s get started!
Understanding Rust and Why You Might Want to Uninstall It
Rust is a powerful systems programming language known for its memory safety and performance. However, there are several reasons why you might need to uninstall Rust:
- Freeing up disk space: Rust installations, including the toolchain and associated files, can consume a significant amount of storage, especially if you have multiple versions installed.
- Resolving conflicts: Sometimes, Rust can conflict with other software or development tools on your system, leading to unexpected errors or instability.
- Switching to a different language: You might be moving on to a different programming language or framework that better suits your current projects.
- Troubleshooting installation issues: If you encounter problems during the initial installation process, a clean uninstall followed by a fresh installation can often resolve these issues.
- No longer needed: Simply put, you may no longer require Rust for your development workflow.
Whatever your reason, it’s crucial to uninstall Rust properly to avoid leaving behind residual files or configurations that could cause problems later. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to do just that.
What is Rust? A Brief Overview
Rust is a multi-paradigm, high-level, general-purpose programming language designed for performance and safety, especially safe concurrency. Rust enforces memory safety without garbage collection, making it useful for a number of use cases where performance is critical. It combines low-level control with high-level ergonomics, making it a popular choice for system programming, embedded systems, and web development.
Why Proper Uninstallation Matters
Improperly uninstalling software, including Rust, can lead to:
- Orphaned files: Files and directories related to Rust might remain on your system, wasting disk space.
- Registry issues: On Windows, leftover registry entries can cause conflicts with other software.
- Path conflicts: Environment variables related to Rust might persist, interfering with other development tools.
- Unpredictable behavior: In some cases, incomplete uninstallation can lead to unexpected errors or instability in other applications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Uninstalling Rust
The recommended method for uninstalling Rust is using the rustup uninstaller. Rustup is the installer and version manager for Rust. It’s the most common way to install Rust, and it provides a simple and reliable way to uninstall Rust as well.
Method 1: Using the Rustup Uninstaller
- Open your terminal or command prompt:
- Windows: Press the Windows key, type “cmd”, and press Enter.
- macOS: Open the “Terminal” application from the “Utilities” folder within “Applications”.
- Linux: Open your preferred terminal emulator.
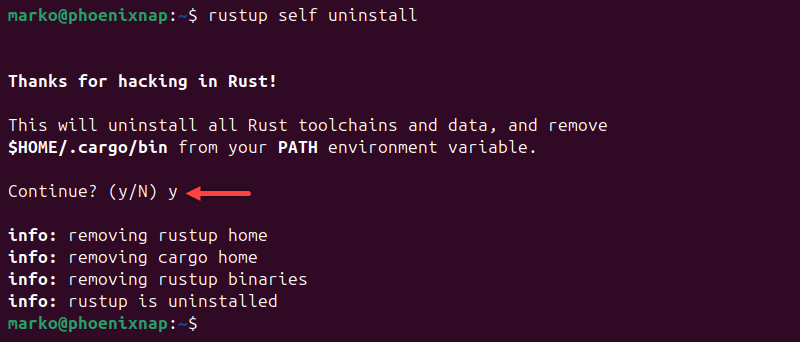
- Run the rustup uninstaller: Type the following command and press Enter:
rustup self uninstall - Confirm the uninstallation: The uninstaller will ask you to confirm that you want to uninstall Rustup and all associated components. Type “y” and press Enter.
- Wait for the process to complete: The uninstaller will remove Rust, Cargo (the Rust package manager), and other related tools and files.
- Verify the uninstallation: After the uninstallation is complete, close and reopen your terminal or command prompt. Then, type
rustc --versionandcargo --version. If Rust and Cargo are no longer installed, you should see an error message indicating that the commands are not recognized.
Method 2: Manual Uninstallation (If Rustup Wasn’t Used)
If you didn’t use Rustup to install Rust, you’ll need to uninstall Rust manually. This involves removing the Rust toolchain, Cargo, and any associated environment variables.
- Locate the Rust installation directory: The location of the Rust installation directory depends on how you installed Rust. Common locations include:
- Windows:
C:Program FilesRust,C:UsersYourUsername.cargobin - macOS:
/usr/local/rust,~/.cargo/bin - Linux:
/usr/local/rust,~/.cargo/bin
- Windows:
- Delete the Rust installation directory: Use your operating system’s file manager to delete the Rust installation directory.
- Remove Cargo’s bin directory from your PATH: The PATH environment variable contains a list of directories where your operating system looks for executable files. You need to remove Cargo’s bin directory from your PATH to prevent conflicts with other software.
- Windows:
- Press the Windows key, type “environment variables”, and press Enter.
- Click the “Environment Variables” button.
- In the “System variables” section, find the “Path” variable and click “Edit”.
- Remove the entry that points to Cargo’s bin directory (e.g.,
C:UsersYourUsername.cargobin). - Click “OK” to save your changes.
- macOS and Linux:
- Open your shell configuration file (e.g.,
~/.bashrc,~/.zshrc). - Remove the line that adds Cargo’s bin directory to your PATH (e.g.,
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.cargo/bin). - Save your changes and close the file.
- Run
source ~/.bashrcorsource ~/.zshrcto apply the changes.
- Open your shell configuration file (e.g.,
- Windows:
- Remove any other Rust-related environment variables: Check your environment variables for any other variables that might be related to Rust (e.g.,
RUST_HOME,RUSTUP_HOME) and remove them. - Verify the uninstallation: After removing the files and environment variables, close and reopen your terminal or command prompt. Then, type
rustc --versionandcargo --version. If Rust and Cargo are no longer installed, you should see an error message indicating that the commands are not recognized.
Troubleshooting Common Uninstall Issues
Even with the rustup uninstaller, you might encounter some issues when trying to uninstall Rust. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Issue 1: Permission Denied Errors
Problem: The uninstaller might fail to remove certain files or directories due to permission issues.
Solution:
- Windows: Run the command prompt as an administrator. Right-click on the command prompt icon and select “Run as administrator”.
- macOS and Linux: Use the
sudocommand to run the uninstaller with elevated privileges. For example:sudo rustup self uninstall
Issue 2: Rust Processes Still Running
Problem: The uninstaller might fail if there are Rust processes still running in the background.
Solution:
- Close any Rust-related applications: Make sure that you’ve closed any applications that might be using Rust, such as IDEs or build tools.
- Kill any running Rust processes: Use your operating system’s task manager or process monitor to identify and kill any running Rust processes (e.g.,
rustc,cargo).
Issue 3: Rustup Not Found
Problem: The rustup command might not be recognized if it’s not in your PATH environment variable.
Solution:
- Add Rustup to your PATH: Make sure that the directory containing the
rustupexecutable is in your PATH environment variable. The default location is~/.cargo/binon macOS and Linux, andC:UsersYourUsername.cargobinon Windows.
Alternatives to Rust
If you’re uninstalling Rust because you’re switching to a different language or framework, here are a few popular alternatives to consider:
- C++: A powerful and versatile language that’s widely used for system programming, game development, and high-performance applications.
- Go: A modern language developed by Google that’s known for its simplicity, concurrency, and performance.
- Python: A high-level language that’s popular for scripting, web development, and data science.
The best language for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as performance, ease of use, and the availability of libraries and frameworks.
Benefits of a Clean Uninstall
Performing a clean uninstall Rust offers several advantages:
- Disk Space: Reclaim valuable storage space by removing unused files and directories.
- System Stability: Avoid potential conflicts and errors that can arise from leftover files or incorrect configurations.
- Clean Slate: Ensure a fresh start if you plan to reinstall Rust or switch to a different development environment.
- Improved Performance: Reduce clutter and improve overall system performance.
Q&A: Advanced Uninstalling Rust Questions
- Q: How do I completely remove Rust from WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux)?
A: The process is similar to uninstalling on a regular Linux system. First, enter your WSL environment. Then, use
rustup self uninstall. Ensure you also remove any Rust-related environment variables set within your WSL’s shell configuration files (e.g., .bashrc, .zshrc). - Q: I’ve uninstalled Rust, but Cargo still seems to be available. Why?
A: This usually happens because the Cargo’s bin directory is still in your PATH environment variable. Follow the steps in the manual uninstallation section to remove it.
- Q: How can I ensure there are no residual Rust files after uninstalling?
A: After using rustup, manually check for any remaining files in common installation directories (e.g.,
~/.cargo,/usr/local/rust). Also, search for files with “rust” or “cargo” in their names using your operating system’s search tool. - Q: Can I uninstall a specific version of Rust while keeping others?
A: Rustup manages multiple toolchains. To remove a specific version, use
rustup uninstall <toolchain>(e.g.,rustup uninstall stable,rustup uninstall nightly). This will remove only the specified version. - Q: What should I do if the rustup uninstaller fails with an error?
A: Try running the uninstaller with elevated privileges (
sudo rustup self uninstallon macOS/Linux, “Run as administrator” on Windows). If that doesn’t work, check the rustup documentation for troubleshooting steps, or consult online forums for solutions. - Q: Does uninstalling Rust remove all packages I installed with Cargo?
A: Uninstalling Rust itself doesn’t automatically remove packages installed with Cargo. These packages are typically stored in the
~/.cargo/registrydirectory. You can manually delete this directory to remove them. - Q: How does uninstalling Rust affect projects I’ve created using it?
A: Uninstalling Rust will prevent you from building or running those projects until you reinstall Rust. The project files themselves will remain untouched.
- Q: Is it safe to delete the .cargo directory after uninstalling Rust?
A: Yes, it is generally safe to delete the
.cargodirectory after uninstalling Rust, as it contains Rust-related configuration files, installed packages, and other data. However, make sure you don’t have any important data stored there that you want to keep. - Q: I get an error regarding environment variables when trying to use other applications after uninstalling Rust. What is happening?
A: This often means that the PATH variable still contains entries related to Rust or Cargo. Review your system’s environment variables and remove any entries pointing to Rust or Cargo directories. Restarting your computer after doing so can also help.
- Q: After uninstalling Rust, my system is still behaving strangely. Could Rust be the cause?
A: It’s unlikely, but possible. Review the steps outlined in this article, and ensure no Rust files or environment variables remain. If problems persist, consider consulting with a technical expert to diagnose further issues.
Conclusion
Successfully uninstalling Rust from your system is a straightforward process when you follow the correct steps. By using the rustup uninstaller or performing a manual uninstallation, you can ensure a clean removal and avoid potential issues. We’ve shared our expertise and experience to provide you with the most comprehensive and trustworthy guide available. Remember to double-check for any residual files or environment variables to ensure a completely clean uninstall.
Now that you’ve successfully uninstall Rust, you can reclaim your system resources and move on to other development endeavors. If you have any further questions or encounter any issues, feel free to share your experiences with uninstall rust in the comments below. Explore our advanced guides to other programming languages for your next project.
