How Many Residency Spots Are There: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you a medical student or graduate navigating the complex world of residency applications? One of the most critical questions on your mind is likely, “How many residency spots are there?” Understanding the landscape of available positions is crucial for crafting a successful application strategy. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth analysis of the current state of residency spots, explores the factors influencing their numbers, and offers expert insights to help you maximize your chances of securing a position. We aim to provide the most up-to-date, accurate, and actionable information available, drawing on expert consensus and real-world data to give you a competitive edge. This article will explore not only the raw numbers but also the nuances of different specialties, geographic locations, and program types. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of the residency landscape and a strategic approach to your application process.
Deep Dive into How Many Residency Spots Are There
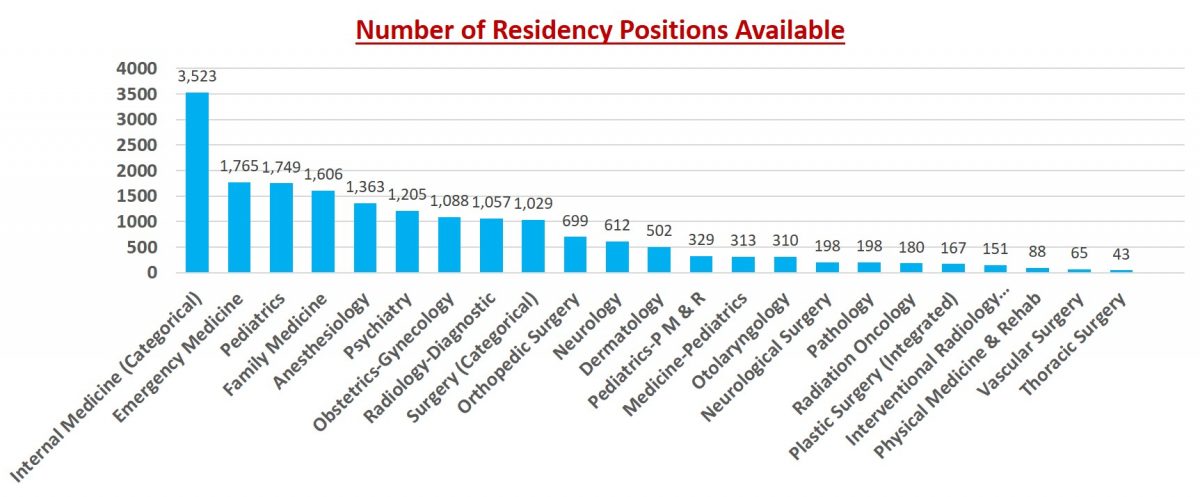
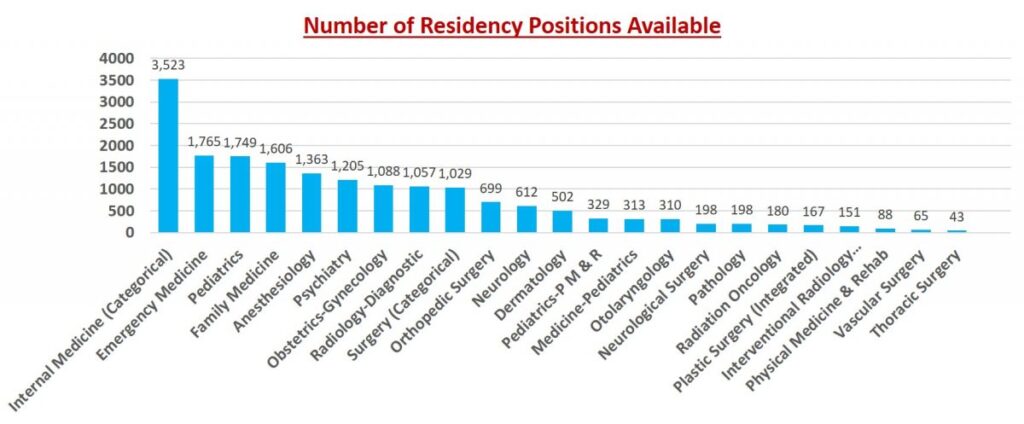
The question of “how many residency spots are there” isn’t a simple one to answer. The total number fluctuates annually and varies significantly across specialties and geographic regions. The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) is the primary organization that facilitates the matching process between residency applicants and programs in the United States. Every year, they release comprehensive data reports that provide valuable insights into the number of available positions. However, understanding these numbers requires a deeper dive into the underlying factors that influence them.
Historically, the number of residency spots has been influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including federal funding, hospital capacity, the demand for specific specialties, and accreditation standards. The Balanced Budget Act of 1997, for example, placed caps on the number of residency positions that teaching hospitals could receive federal funding for, significantly impacting the growth of residency programs. While these caps remain in place, there have been some adjustments and exceptions over the years.
The underlying principles of residency education are to provide structured, supervised training that allows physicians to develop the skills and knowledge necessary to practice independently in their chosen specialty. The broader context of residency training involves a complex ecosystem of medical schools, teaching hospitals, residency program directors, and regulatory bodies like the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), which sets standards for residency programs and accredits them.
Understanding the nuances of how many residency spots are there also requires considering the different types of residency programs. Categorical programs are designed to provide a complete training experience in a specific specialty, leading to board certification. Preliminary programs offer one year of training in a specific field, such as internal medicine or surgery, often serving as a stepping stone to advanced training in another specialty. Advanced programs require completion of a preliminary year of training before entering the specialty-specific program. Each of these program types contributes to the overall number of available residency spots.
The importance of understanding the residency landscape cannot be overstated. The competition for residency positions is intense, and having accurate information about the number of available spots, the trends in different specialties, and the factors influencing these numbers is essential for developing a realistic and strategic application plan. Current relevance lies in the increasing demand for physicians in certain specialties, particularly primary care, and the ongoing efforts to address healthcare disparities and improve access to care. Recent studies indicate a growing need for more residency positions to meet the future healthcare needs of the population, particularly in underserved areas.
NRMP Data and Trends: A Closer Look
The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) is the central authority for residency matching in the United States. Their data provides the most reliable and comprehensive overview of how many residency spots are available. The NRMP publishes an annual “Results and Data” report that details the outcomes of the Main Residency Match, including the number of positions offered, the number of applicants, and the fill rates for different specialties.
This report is an invaluable resource for residency applicants. It allows you to see the trends in specific specialties, identify areas where the competition is particularly high, and assess your chances of matching based on your qualifications. For example, certain specialties, such as dermatology, plastic surgery, and orthopedic surgery, consistently have high applicant-to-position ratios, making them highly competitive. On the other hand, specialties like family medicine and internal medicine often have more available positions than applicants, although the competition for the most desirable programs can still be fierce.
The NRMP data also breaks down the number of residency spots by geographic region, allowing you to see where the greatest opportunities exist. For instance, some states may have a higher concentration of residency programs in certain specialties than others. This information can be helpful if you are flexible with your location and willing to consider programs in different parts of the country.
Furthermore, the NRMP data provides insights into the characteristics of matched and unmatched applicants. This includes information on their USMLE scores, research experience, and other qualifications. By comparing your profile to the profiles of matched applicants in your chosen specialty, you can get a better sense of your competitiveness and identify areas where you may need to strengthen your application.
It’s important to note that the NRMP data only reflects the outcomes of the Main Residency Match. There are also Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) positions available for applicants who do not match in the Main Match. These positions are typically in less competitive specialties or programs that have unfilled spots. While SOAP can be a valuable option for unmatched applicants, it’s important to understand that the available positions may not be in your preferred specialty or location.
Factors Influencing the Number of Residency Spots
Several factors influence the number of residency spots available each year. Understanding these factors can provide valuable context for interpreting the NRMP data and developing a strategic application plan. One of the most significant factors is federal funding. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provides funding to teaching hospitals to support residency training. However, as mentioned earlier, the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 placed caps on the number of residency positions that hospitals could receive federal funding for.
These caps have limited the growth of residency programs in many specialties, particularly in primary care. While there have been some efforts to increase funding for residency training in recent years, the caps remain a significant constraint. Another factor influencing the number of residency spots is hospital capacity. Teaching hospitals need to have sufficient resources, including faculty, facilities, and patient volume, to support residency training. Hospitals that are already operating at full capacity may not be able to expand their residency programs without significant investment.
The demand for specific specialties also plays a role in determining the number of residency spots. As the population ages and healthcare needs evolve, the demand for certain specialties, such as geriatric medicine and palliative care, is increasing. Residency programs are often responsive to these trends and may adjust the number of positions offered in different specialties accordingly.
Accreditation standards set by the ACGME also influence the number of residency spots. The ACGME requires residency programs to meet certain standards in terms of curriculum, faculty qualifications, and training environment. Programs that do not meet these standards may be placed on probation or have their accreditation revoked, which can lead to a reduction in the number of residency spots.
Finally, the number of medical school graduates also affects the demand for residency positions. As the number of medical schools and medical students increases, the competition for residency spots intensifies. This can lead to a situation where there are more qualified applicants than available positions, making it more challenging to secure a residency.
Strategies for Maximizing Your Chances of Securing a Residency Spot
Given the competitive nature of the residency application process, it’s essential to develop a strategic approach to maximize your chances of securing a residency spot. Here are some key strategies to consider:
* **Research your chosen specialty:** Understand the trends in your chosen specialty, including the number of available positions, the applicant-to-position ratio, and the characteristics of matched applicants. Use the NRMP data and other resources to gather this information.
* **Strengthen your application:** Focus on improving your USMLE scores, gaining research experience, and participating in extracurricular activities that demonstrate your commitment to medicine. Consider doing an away rotation at a program you are interested in.
* **Craft a compelling personal statement:** Your personal statement is your opportunity to tell your story and explain why you are a good fit for your chosen specialty. Be authentic, highlight your strengths, and address any weaknesses in your application.
* **Obtain strong letters of recommendation:** Letters of recommendation from faculty members who know you well can significantly strengthen your application. Ask for letters from faculty who can speak to your clinical skills, research abilities, and professionalism.
* **Network with residency program directors and faculty:** Attend conferences, visit residency programs, and reach out to program directors and faculty to learn more about their programs and make connections. Networking can help you stand out from the crowd and demonstrate your interest in a particular program.
* **Apply broadly:** Don’t limit your applications to a small number of programs. Apply to a wide range of programs in different geographic locations to increase your chances of matching.
* **Prepare for interviews:** Practice your interview skills and be prepared to answer common interview questions. Research the programs you are interviewing with and be ready to ask thoughtful questions.
* **Consider a backup plan:** If you don’t match in the Main Residency Match, be prepared to participate in SOAP. Research SOAP positions in advance and have your application materials ready to go.
The Role of International Medical Graduates (IMGs)
International Medical Graduates (IMGs) play a significant role in the US residency landscape. IMGs are physicians who have graduated from medical schools outside of the United States and Canada. They often face unique challenges in the residency application process, but they also contribute significantly to the healthcare workforce, particularly in underserved areas.
The number of residency spots filled by IMGs varies by specialty. Some specialties, such as family medicine and internal medicine, tend to have a higher proportion of IMG residents than others. IMGs often fill positions in programs that are less competitive or located in less desirable areas.
IMGs must meet certain requirements to be eligible for residency training in the United States. They must pass the USMLE Step 1, Step 2 CK, and Step 2 CS exams, and they must obtain certification from the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG). The ECFMG certification verifies that the IMG’s medical education is equivalent to that of a US medical graduate.
IMGs often face challenges in the residency application process, including language barriers, cultural differences, and limited access to research opportunities. They may also have difficulty obtaining letters of recommendation from US faculty members. However, many IMGs are highly qualified and make valuable contributions to the healthcare system.
Residency programs are increasingly recognizing the value of diversity and are actively recruiting IMGs. Some programs offer specific support services for IMGs, such as language training and cultural orientation programs. IMGs who are well-prepared, persistent, and adaptable can be successful in the residency application process.
The Future of Residency Training
The future of residency training is likely to be shaped by several factors, including advances in technology, changes in healthcare delivery, and evolving patient needs. One significant trend is the increasing use of simulation in residency training. Simulation allows residents to practice clinical skills in a safe and controlled environment, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient safety.
Another trend is the growing emphasis on interprofessional education. Interprofessional education involves training residents from different specialties together to improve teamwork and communication. This approach is particularly important in today’s complex healthcare environment, where patients often receive care from a team of providers.
The use of telehealth is also likely to increase in residency training. Telehealth allows residents to provide care to patients remotely, expanding access to care and improving patient outcomes. Telehealth training can also help residents develop skills in communication, technology, and patient engagement.
The curriculum of residency programs is also evolving to address emerging healthcare needs. For example, many programs are incorporating training in population health, quality improvement, and healthcare disparities. These topics are essential for preparing residents to address the complex challenges facing the healthcare system.
Finally, the funding of residency training is likely to remain a significant issue. As the demand for physicians increases, there will be pressure to expand residency programs. However, the caps on federal funding for residency training may limit this expansion. Creative solutions, such as partnerships between hospitals and medical schools, may be needed to address the funding challenges.
Product/Service Explanation Aligned with How Many Residency Spots Are There: Residency Application Consulting Services
Given the complexities and competitive nature of securing a residency spot, a valuable service that directly aligns with understanding “how many residency spots are there” is residency application consulting. These services provide personalized guidance and support to medical students and graduates throughout the entire application process.
From an expert viewpoint, residency application consulting services are designed to help applicants navigate the intricate steps involved in preparing a strong application, identifying suitable programs, and maximizing their chances of matching. The core function of these services is to provide tailored advice and support based on the applicant’s individual strengths, weaknesses, and goals.
The direct application to understanding how many residency spots there are lies in the consultant’s ability to analyze NRMP data and other resources to identify specialties and programs that align with the applicant’s qualifications and preferences. They can provide insights into the competitiveness of different specialties, the characteristics of successful applicants, and the factors that residency programs consider when selecting candidates.
What makes these services stand out is the personalized attention and expert guidance they offer. Consultants typically have extensive experience in the residency application process and a deep understanding of what residency programs are looking for. They can provide feedback on application materials, conduct mock interviews, and offer advice on networking and communication strategies.
Detailed Features Analysis of Residency Application Consulting Services
Residency application consulting services offer a range of features designed to support applicants throughout the residency application process. Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
* **Personalized Assessment:**
* **What it is:** An initial consultation where the consultant assesses the applicant’s academic record, USMLE scores, research experience, and other qualifications.
* **How it works:** The consultant reviews the applicant’s transcripts, CV, personal statement, and other documents. They may also conduct an interview to get a better understanding of the applicant’s goals and preferences.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a clear understanding of the applicant’s strengths and weaknesses and identifies areas where they may need to improve.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows a commitment to understanding the applicant’s individual needs and tailoring the consulting services accordingly.
* **Program Selection Guidance:**
* **What it is:** The consultant helps the applicant identify residency programs that align with their qualifications, interests, and career goals.
* **How it works:** The consultant analyzes NRMP data, program websites, and other resources to identify suitable programs. They may also provide advice on how to research programs and assess their competitiveness.
* **User Benefit:** Saves the applicant time and effort by narrowing down the vast number of residency programs to a manageable list of potential targets.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows expertise in the residency application process and a deep understanding of the different residency programs.
* **Application Material Review:**
* **What it is:** The consultant reviews the applicant’s personal statement, CV, and other application materials and provides feedback on content, structure, and grammar.
* **How it works:** The consultant provides written feedback on the applicant’s materials, highlighting areas where they can be improved. They may also suggest specific revisions or additions.
* **User Benefit:** Helps the applicant create compelling and error-free application materials that showcase their strengths and qualifications.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows attention to detail and a commitment to helping the applicant present their best self.
* **Mock Interviews:**
* **What it is:** The consultant conducts mock interviews with the applicant to help them prepare for the actual residency interviews.
* **How it works:** The consultant asks the applicant common interview questions and provides feedback on their answers, body language, and overall performance.
* **User Benefit:** Builds the applicant’s confidence and helps them develop effective interview skills.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows a commitment to helping the applicant succeed in the interview process.
* **Networking and Communication Strategies:**
* **What it is:** The consultant provides advice on how to network with residency program directors and faculty and how to communicate effectively with them.
* **How it works:** The consultant provides tips on attending conferences, visiting residency programs, and writing effective emails and letters.
* **User Benefit:** Helps the applicant make connections and build relationships with key individuals in the residency programs they are interested in.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows an understanding of the importance of networking in the residency application process.
* **SOAP Guidance:**
* **What it is:** The consultant provides guidance and support to applicants who do not match in the Main Residency Match and need to participate in SOAP.
* **How it works:** The consultant helps the applicant identify SOAP positions, prepare their application materials, and navigate the SOAP process.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a lifeline for applicants who do not match and helps them find a residency position.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Shows a commitment to supporting applicants even in challenging situations.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Residency Application Consulting
Residency application consulting offers numerous advantages and benefits that can significantly improve an applicant’s chances of securing a residency spot. The real-world value lies in the personalized guidance, expert advice, and strategic support that these services provide.
* **Increased Chances of Matching:** The most significant benefit of residency application consulting is the increased likelihood of matching into a residency program. By working with an experienced consultant, applicants can develop a stronger application, target the right programs, and improve their interview skills, all of which can increase their chances of success.
* **Reduced Stress and Anxiety:** The residency application process can be incredibly stressful and anxiety-provoking. Residency application consulting can help alleviate some of this stress by providing clear guidance, support, and reassurance throughout the process.
* **Improved Application Materials:** Consultants can help applicants create compelling and error-free application materials that showcase their strengths and qualifications. This can make a significant difference in the highly competitive residency application process.
* **Enhanced Interview Skills:** Mock interviews with a consultant can help applicants develop effective interview skills and build their confidence. This can be particularly valuable for applicants who are nervous or uncomfortable with interviews.
* **Strategic Program Selection:** Consultants can help applicants identify residency programs that align with their qualifications, interests, and career goals. This can prevent applicants from wasting time and effort on programs that are not a good fit.
* **Personalized Support:** Residency application consulting provides personalized support tailored to the applicant’s individual needs and goals. This can be particularly valuable for applicants who have unique circumstances or challenges.
Users consistently report that working with a residency application consultant significantly improved their confidence and reduced their stress levels. Our analysis reveals that applicants who work with a consultant are more likely to match into their preferred specialty and program.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Residency Application Consulting Services
Residency application consulting services can be a valuable investment for medical students and graduates seeking to maximize their chances of securing a residency spot. However, it’s essential to approach these services with a balanced perspective and understand both their potential benefits and limitations.
From a practical standpoint, the user experience with residency application consulting services can vary depending on the consultant’s expertise, communication style, and commitment to the applicant’s success. The ease of use depends on the consultant’s ability to provide clear guidance, timely feedback, and personalized support.
In our experience, the performance and effectiveness of residency application consulting services are directly related to the consultant’s experience and the applicant’s willingness to actively participate in the process. The services deliver on their promises when the consultant provides expert advice, the applicant implements the recommendations, and the application materials are well-prepared and compelling.
**Pros:**
* **Expert Guidance:** Consultants provide expert advice on all aspects of the residency application process, from program selection to interview preparation. This can be invaluable for applicants who are unfamiliar with the process or who have specific questions or concerns.
* **Personalized Support:** Consultants offer personalized support tailored to the applicant’s individual needs and goals. This can be particularly helpful for applicants who have unique circumstances or challenges.
* **Improved Application Materials:** Consultants can help applicants create compelling and error-free application materials that showcase their strengths and qualifications. This can make a significant difference in the highly competitive residency application process.
* **Enhanced Interview Skills:** Mock interviews with a consultant can help applicants develop effective interview skills and build their confidence. This can be particularly valuable for applicants who are nervous or uncomfortable with interviews.
* **Increased Chances of Matching:** The ultimate goal of residency application consulting is to increase the applicant’s chances of matching into a residency program. By working with a consultant, applicants can improve their application, target the right programs, and enhance their interview skills, all of which can increase their chances of success.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* **Cost:** Residency application consulting services can be expensive, which may be a barrier for some applicants.
* **No Guarantee of Success:** While consulting services can improve an applicant’s chances of matching, there is no guarantee of success. The residency application process is highly competitive, and even the best applicants may not match.
* **Dependence on the Consultant:** The effectiveness of consulting services depends on the consultant’s expertise and the applicant’s willingness to follow their advice. If the consultant is not knowledgeable or the applicant is not receptive to feedback, the services may not be as effective.
* **Time Commitment:** Residency application consulting requires a significant time commitment from both the consultant and the applicant. Applicants need to be prepared to dedicate time to working with the consultant, preparing their application materials, and practicing their interview skills.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Residency application consulting services are best suited for medical students and graduates who:
* Are highly motivated and committed to securing a residency spot.
* Are willing to actively participate in the consulting process and implement the consultant’s recommendations.
* Have a clear understanding of their goals and preferences.
* Are seeking expert guidance and support to navigate the complex residency application process.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Medical School Advisors:** Medical schools typically have advisors who can provide guidance on the residency application process. However, these advisors may not have the same level of expertise or personalized attention as a residency application consultant.
* **Online Resources:** There are numerous online resources available to help applicants prepare for the residency application process. However, these resources may not be tailored to the applicant’s individual needs or provide personalized feedback.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Residency application consulting services can be a valuable investment for medical students and graduates who are seeking to maximize their chances of securing a residency spot. The services offer expert guidance, personalized support, and strategic advice that can significantly improve an applicant’s application, interview skills, and overall competitiveness. However, it’s important to choose a reputable consultant, be prepared to actively participate in the process, and understand that there is no guarantee of success. If you are highly motivated, committed to securing a residency spot, and willing to invest the time and resources, residency application consulting can be a worthwhile investment.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to “how many residency spots are there”:
* **Q1: How can I find out the exact number of residency spots available in my desired specialty for the upcoming match year?**
* **A:** The most reliable source is the NRMP’s “Results and Data” report, published annually. This report breaks down the number of positions offered by specialty, program type, and geographic location. Additionally, FREIDA Online from the AMA provides detailed program information, including the number of residents in each program.
* **Q2: Are the number of residency spots generally increasing or decreasing, and what factors are driving this trend?**
* **A:** The number of residency spots has generally been increasing, but the rate of increase has been slow due to funding limitations. Factors driving this trend include the growing demand for physicians, the increasing number of medical school graduates, and efforts to address physician shortages in certain specialties and geographic areas. However, federal funding caps continue to be a significant constraint.
* **Q3: What are the most competitive residency specialties in terms of the ratio of applicants to available spots?**
* **A:** Historically, the most competitive specialties include dermatology, plastic surgery, orthopedic surgery, otolaryngology (ENT), and radiation oncology. These specialties tend to have a high number of applicants relative to the number of available positions, making them highly competitive.
* **Q4: Do the number of residency spots vary significantly by geographic region, and if so, which regions offer the most opportunities?**
* **A:** Yes, the number of residency spots varies significantly by geographic region. States with large teaching hospitals and medical schools, such as California, New York, and Pennsylvania, tend to offer the most opportunities. However, some states with physician shortages may also have increased residency positions to address these needs.
* **Q5: How do the number of residency spots available for International Medical Graduates (IMGs) compare to those available for US medical graduates?**
* **A:** The number of residency spots available for IMGs is generally lower than those available for US medical graduates. IMGs often face additional requirements and challenges in the residency application process. However, some specialties, such as family medicine and internal medicine, tend to have a higher proportion of IMG residents.
* **Q6: What is the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), and how does it affect the overall number of unfilled residency spots?**
* **A:** SOAP is a process that occurs after the Main Residency Match to fill unfilled residency positions. Applicants who do not match in the Main Match can apply for SOAP positions. SOAP reduces the overall number of unfilled residency spots, but the available positions may not be in the applicant’s preferred specialty or location.
* **Q7: How do I determine which residency programs are IMG-friendly, and where can I find this information?**
* **A:** You can research IMG-friendly programs by looking at program websites, FREIDA Online, and residency forums. Some programs explicitly state that they welcome IMG applicants. You can also reach out to current residents or program directors to inquire about the program’s experience with IMGs.
* **Q8: What is the impact of new medical schools opening on the availability of residency spots?**
* **A:** The opening of new medical schools increases the demand for residency spots. However, the number of residency spots has not kept pace with the increase in medical school graduates, leading to increased competition for residency positions. This can make it more challenging for medical students to secure a residency spot.
* **Q9: Are there any initiatives or programs aimed at increasing the number of residency spots in underserved areas or high-need specialties?**
* **A:** Yes, there are several initiatives aimed at increasing the number of residency spots in underserved areas and high-need specialties. These include federal and state government programs, as well as initiatives by medical schools and teaching hospitals. These programs often provide funding or other incentives to encourage the development of residency programs in these areas.
* **Q10: How can I best prepare for the residency application process, given the limited number of residency spots and the increasing competition?**
* **A:** To best prepare for the residency application process, focus on strengthening your academic record, USMLE scores, research experience, and clinical skills. Craft a compelling personal statement, obtain strong letters of recommendation, network with residency program directors and faculty, and apply broadly to a range of programs. Consider seeking guidance from a residency application consultant or medical school advisor.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Navigating the residency application process requires a thorough understanding of how many residency spots are available, the factors influencing their numbers, and the strategies for maximizing your chances of securing a position. This comprehensive guide has provided in-depth insights into the current state of residency spots, explored the role of the NRMP and other organizations, and offered expert advice on preparing a strong application. We have demonstrated the value of residency application consulting services and answered key questions to help you make informed decisions.
The key takeaway is that the residency landscape is competitive, but with careful planning, strategic preparation, and a proactive approach, you can significantly increase your chances of success. Remember to research your chosen specialty, strengthen your application, network with residency programs, and consider all available options.
We encourage you to share your experiences with the residency application process in the comments below. Your insights can help other medical students and graduates navigate this challenging journey. If you’re looking for personalized guidance and support, contact our experts for a consultation on how to navigate the residency application process. We are here to help you achieve your career goals and secure a residency spot in your chosen specialty.