NY State Medical Board: Your Comprehensive Guide to Licensing & Regulation
Are you a physician seeking licensure in New York State? Or perhaps a patient wanting to understand the standards of medical care and physician oversight? Navigating the complexities of the **NY State Medical Board** can be daunting. This comprehensive guide provides everything you need to know, from licensing requirements and disciplinary processes to patient rights and resources. We aim to empower you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the New York medical landscape. This guide offers unparalleled depth, expert insights, and practical advice based on years of experience observing and interacting with the Board’s regulations and processes.
What is the NY State Medical Board? A Deep Dive
The **NY State Medical Board**, officially known as the New York State Board for Professional Medical Conduct (BPMC), is a critical entity responsible for overseeing the practice of medicine within New York. It’s a division of the New York State Education Department (NYSED) and plays a pivotal role in ensuring that physicians meet established standards of competence, conduct, and patient care. The board’s authority stems from the New York State Education Law, which grants it the power to license, regulate, and discipline medical professionals.
Historically, the Board has evolved to address the changing needs of the medical field and the public. Initially focused primarily on licensing, its scope has expanded to include rigorous monitoring of physician conduct, addressing issues such as medical malpractice, ethical violations, and substance abuse. This evolution reflects a growing emphasis on patient safety and accountability within the medical profession.
The BPMC operates under the guiding principle of protecting the public health, safety, and welfare. It achieves this by:
* **Licensing qualified physicians:** Ensuring that only those who meet stringent educational, examination, and character requirements are authorized to practice medicine in New York.
* **Setting standards of practice:** Establishing guidelines and expectations for physician conduct and patient care.
* **Investigating complaints:** Thoroughly examining allegations of misconduct or negligence against physicians.
* **Disciplining physicians:** Imposing appropriate sanctions on those found to have violated the law or ethical standards, ranging from warnings and fines to license suspension or revocation.
* **Monitoring compliance:** Ensuring that physicians adhere to disciplinary orders and maintain ongoing competence.
Recent trends indicate a heightened focus on issues such as opioid prescribing practices, telehealth regulations, and the impact of technology on patient care. The Board is constantly adapting to these changes, updating its policies and procedures to reflect best practices and ensure patient safety in a rapidly evolving healthcare environment.
Licensing & Certification: Your Path to Practicing Medicine in NY
Obtaining a medical license in New York State requires a meticulous process. The NY State Medical Board sets specific requirements that must be met to ensure that all licensed physicians have the necessary qualifications and ethical standards to provide safe and effective patient care. The process involves several key steps:
1. **Educational Requirements:** Applicants must have graduated from an accredited medical school. Graduates of foreign medical schools must also meet additional requirements, such as completing a clinical clerkship in the United States.
2. **Examination Requirements:** Candidates must pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) or the Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX-USA). Specific score requirements must be met.
3. **Application Process:** A detailed application must be submitted to the NY State Education Department, including transcripts, examination scores, and other supporting documentation.
4. **Background Check:** All applicants undergo a thorough background check to assess their moral character and fitness to practice medicine.
5. **Fees:** Application and licensing fees must be paid.
Maintaining your license also requires ongoing effort. Physicians must complete continuing medical education (CME) requirements to stay up-to-date with the latest advances in medicine. License renewal is required periodically, and physicians must attest to their compliance with CME requirements and ethical standards.
The NY State Medical Board also offers various certifications for specialized medical fields. These certifications demonstrate advanced training and expertise in a specific area of medicine. Requirements for certification vary depending on the specialty but generally include completing a residency program and passing a specialty board examination.
The Disciplinary Process: Ensuring Accountability
The NY State Medical Board is committed to holding physicians accountable for their actions. The disciplinary process is designed to investigate and address allegations of misconduct or negligence. This process typically involves the following steps:
1. **Complaint Filing:** Any individual, including patients, colleagues, or healthcare organizations, can file a complaint against a physician with the Office of Professional Medical Conduct (OPMC).
2. **Investigation:** The OPMC investigates the complaint, gathering evidence and interviewing witnesses. The physician has the right to respond to the allegations.
3. **Review and Determination:** The OPMC reviews the evidence and determines whether there is sufficient evidence to support the allegations. If so, the case may be referred to a hearing.
4. **Hearing:** A hearing is held before a panel of the State Board for Professional Medical Conduct. The physician has the right to present evidence and legal representation.
5. **Decision and Sanctions:** The hearing panel makes a decision based on the evidence presented. If the physician is found guilty of misconduct, sanctions may be imposed, ranging from warnings and fines to license suspension or revocation.
Common causes for disciplinary action include medical malpractice, substance abuse, ethical violations, and unprofessional conduct. Physicians have the right to appeal disciplinary decisions through the court system.
Patient Rights & Resources: Empowering Patients in New York
Patients in New York have specific rights when receiving medical care. These rights are protected by law and enforced by the NY State Medical Board. Key patient rights include:
* **The right to informed consent:** Patients have the right to receive information about their medical condition, proposed treatment options, and potential risks and benefits before making a decision about their care.
* **The right to confidentiality:** Patients have the right to have their medical information kept confidential.
* **The right to access medical records:** Patients have the right to access and review their medical records.
* **The right to a second opinion:** Patients have the right to seek a second opinion from another physician.
* **The right to file a complaint:** Patients have the right to file a complaint against a physician if they believe they have been subjected to substandard care or misconduct.
Various resources are available to help patients navigate the healthcare system and exercise their rights. The NY State Department of Health and the NY State Medical Board provide information and assistance to patients. Patient advocacy groups can also provide support and guidance. Understanding your rights and accessing available resources is crucial for ensuring that you receive the best possible medical care.
Navigating the NY State Medical Board Website: A User’s Guide
The NY State Medical Board’s website is a vital resource for physicians and patients alike. It provides access to information about licensing, regulations, disciplinary actions, and other important topics. Navigating the website effectively can save you time and effort. Here’s a breakdown of key features and how to use them:
* **Licensing Information:** Find detailed information about licensing requirements, application procedures, and renewal processes.
* **Disciplinary Actions:** Access records of disciplinary actions taken against physicians, including the reasons for the actions and the sanctions imposed.
* **Laws and Regulations:** Review the laws and regulations governing the practice of medicine in New York.
* **Forms and Applications:** Download necessary forms and applications for licensing, renewal, and other purposes.
* **Contact Information:** Find contact information for the NY State Medical Board and other relevant agencies.
* **Search Functionality:** Use the search function to quickly find specific information on the website.
For example, if you are a physician seeking to renew your license, you can find the renewal application and instructions on the website. If you are a patient looking for information about a specific physician, you can search for disciplinary actions taken against that physician. The website is designed to be user-friendly, but if you have any questions, you can contact the NY State Medical Board for assistance.
Expert Insights: Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
Navigating the NY State Medical Board’s processes can be challenging. Based on our observations and interactions with physicians and patients, here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
* **Incomplete Applications:** Ensure that your application is complete and accurate. Missing information can delay the processing of your application.
* **Failure to Meet CME Requirements:** Keep track of your CME credits and ensure that you meet the requirements for license renewal.
* **Ethical Violations:** Adhere to ethical standards and avoid any actions that could be perceived as unprofessional conduct.
* **Lack of Communication:** Respond promptly to any inquiries from the NY State Medical Board or the OPMC.
* **Failure to Seek Legal Advice:** If you are facing disciplinary action, seek legal advice from an attorney experienced in medical board matters.
For instance, we’ve seen several cases where physicians faced delays in their license renewal due to incomplete applications. Taking the time to carefully review your application and ensure that all required information is included can prevent such delays.
Telemedicine and the NY State Medical Board: Regulations and Guidelines
Telemedicine is transforming healthcare, and the NY State Medical Board is actively addressing its implications. The Board has established regulations and guidelines to ensure that telemedicine services are provided safely and effectively. Key aspects of telemedicine regulation include:
* **Licensing Requirements:** Physicians providing telemedicine services to patients in New York must be licensed in New York.
* **Standard of Care:** Physicians providing telemedicine services must adhere to the same standard of care as physicians providing in-person care.
* **Patient Consent:** Patients must provide informed consent before receiving telemedicine services.
* **Confidentiality:** Patient confidentiality must be protected in telemedicine interactions.
* **Technology Requirements:** Telemedicine platforms must meet certain technical requirements to ensure security and privacy.
The NY State Medical Board is constantly updating its telemedicine regulations to keep pace with technological advancements. Recent changes include expanding the types of services that can be provided via telemedicine and addressing issues such as reimbursement and interstate practice. Staying informed about the latest telemedicine regulations is crucial for physicians providing these services.
The Future of Medical Regulation in New York: Trends to Watch
The NY State Medical Board is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of the healthcare system. Several trends are likely to shape the future of medical regulation in New York:
* **Increased Emphasis on Patient Safety:** Patient safety will continue to be a top priority, with stricter enforcement of regulations and increased accountability for physicians.
* **Expansion of Telemedicine:** Telemedicine will continue to grow, leading to further development of regulations and guidelines.
* **Focus on Opioid Prescribing:** The opioid crisis will continue to be a major concern, with stricter monitoring of opioid prescribing practices.
* **Integration of Technology:** Technology will play an increasingly important role in medical regulation, with the use of electronic health records and data analytics to monitor physician performance.
* **Collaboration with Other Agencies:** The NY State Medical Board will continue to collaborate with other agencies to address complex healthcare issues.
By staying informed about these trends, physicians and patients can better prepare for the future of medical regulation in New York.
Q&A: Your Burning Questions Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about the NY State Medical Board:
**Q1: What is the difference between the NY State Medical Board and the Office of Professional Medical Conduct (OPMC)?**
A: The NY State Medical Board, technically the Board for Professional Medical Conduct (BPMC), is the overall entity responsible for licensing and regulating physicians. The OPMC is the investigative arm of the Board, responsible for investigating complaints and prosecuting cases of misconduct.
**Q2: How can I find out if a physician has been disciplined by the NY State Medical Board?**
A: You can search for disciplinary actions on the NY State Medical Board’s website. Disciplinary records are public information.
**Q3: What should I do if I believe I have been the victim of medical malpractice?**
A: You should consult with an attorney experienced in medical malpractice cases. They can advise you on your legal options.
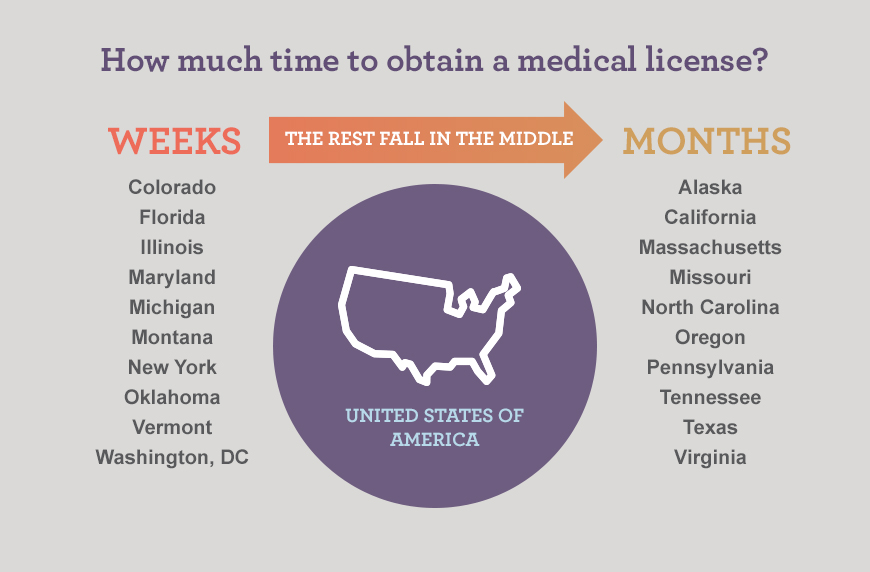
**Q4: How long does it take to get a medical license in New York?**
A: The processing time for medical license applications varies depending on the completeness of the application and the volume of applications being processed. It can take several months.
**Q5: What are the CME requirements for maintaining a medical license in New York?**
A: Physicians must complete a certain number of CME credits every two years to maintain their license. The specific requirements vary depending on the specialty.
**Q6: Can I practice telemedicine in New York if I am licensed in another state?**
A: Generally, you must be licensed in New York to practice telemedicine with patients in New York. However, there may be exceptions in certain circumstances.
**Q7: How can I file a complaint against a physician?**
A: You can file a complaint with the Office of Professional Medical Conduct (OPMC).
**Q8: What types of disciplinary actions can the NY State Medical Board take against a physician?**
A: The Board can impose sanctions ranging from warnings and fines to license suspension or revocation.
**Q9: Are there any resources available to help me understand my rights as a patient?**
A: Yes, the NY State Department of Health and patient advocacy groups can provide information and assistance.
**Q10: How does the NY State Medical Board address issues related to opioid prescribing?**
A: The Board has implemented stricter monitoring of opioid prescribing practices and has taken disciplinary actions against physicians who have violated prescribing guidelines.
Conclusion: Navigating the New York Medical Landscape with Confidence
The **NY State Medical Board** plays a critical role in ensuring the quality and safety of medical care in New York. Understanding its functions, processes, and regulations is essential for both physicians and patients. By staying informed, adhering to ethical standards, and exercising your rights, you can confidently navigate the New York medical landscape. As we’ve seen, the Board is constantly evolving to address new challenges and opportunities in healthcare. We encourage you to explore the resources mentioned in this guide and stay up-to-date with the latest developments. Share your experiences with the NY State Medical Board in the comments below, or contact our experts for a consultation on specific licensing or disciplinary matters.
