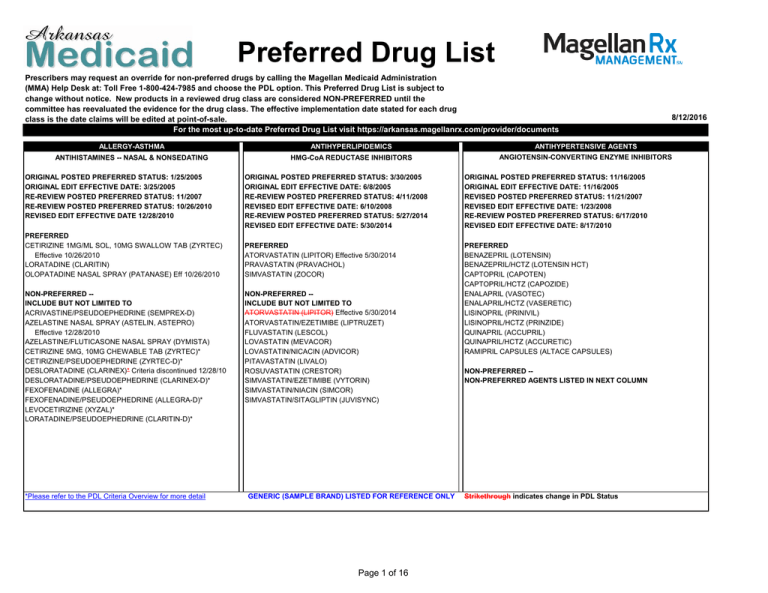
# New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List: Your Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Your Medications
Navigating the complexities of healthcare can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding your prescription medications. If you are a New York Medicaid recipient, understanding the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List (PDL) is crucial to accessing the medications you need while managing costs. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide you with an in-depth understanding of the New York Medicaid PDL, empowering you to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
This article will explore every facet of the PDL, from its core principles and how it functions, to its benefits, potential drawbacks, and how it impacts your access to medications. We will also discuss finding information about specific drugs on the list and steps to take if a needed medication isn’t preferred. We’ll answer frequently asked questions and offer expert insights to help you navigate the system effectively.
## Understanding the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List
The New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List (PDL) is a list of prescription medications that are preferred by New York Medicaid. This means that these drugs are generally covered without requiring prior authorization, making them more accessible to Medicaid recipients. The PDL is designed to encourage the use of cost-effective medications while ensuring that patients have access to the drugs they need.
### Core Concepts and Principles of the PDL
The PDL operates on several core principles:
* **Cost-Effectiveness:** The PDL prioritizes medications that provide the best value for the state, considering both their effectiveness and cost. This helps to control healthcare spending and ensure that Medicaid resources are used efficiently.
* **Therapeutic Equivalence:** The PDL considers therapeutic equivalence, meaning that preferred drugs are generally those that are clinically similar to other drugs in the same class. This ensures that patients have access to effective treatment options.
* **Clinical Evidence:** The PDL is based on clinical evidence and expert recommendations. The list is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the latest medical research and best practices. The Drug Utilization Review (DUR) Board plays a key role in this process.
* **Prior Authorization (PA):** If a medication is *not* on the PDL, it may require prior authorization. This means your doctor needs to get approval from Medicaid before you can get the medication covered. The PA process ensures that non-preferred drugs are used when medically necessary.
### History and Evolution of the PDL
The New York Medicaid PDL has evolved over time to adapt to changing healthcare needs and advancements in medical science. The list is regularly updated based on the recommendations of the Drug Utilization Review (DUR) Board, which comprises physicians, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals. These updates ensure that the PDL remains current and reflects the latest clinical evidence.
The PDL’s evolution also reflects the ongoing effort to balance cost containment with patient access to necessary medications. New York has implemented various strategies to manage drug costs, including negotiating rebates with pharmaceutical manufacturers and promoting the use of generic drugs.
### Importance and Current Relevance
The New York Medicaid PDL is crucial for several reasons:
* **Access to Medications:** It ensures that Medicaid recipients have access to a wide range of prescription medications.
* **Cost Savings:** It helps control healthcare costs by encouraging the use of cost-effective drugs.
* **Quality of Care:** It promotes the use of medications that are clinically effective and safe, based on the latest medical evidence.
In 2024, the PDL remains highly relevant as healthcare costs continue to rise. New York Medicaid relies on the PDL to manage its prescription drug expenditures and ensure that resources are used efficiently. Understanding the PDL is essential for both healthcare providers and Medicaid recipients to make informed decisions about medication choices.
## How the PDL Impacts Your Medication Access
The PDL directly impacts which medications are readily available to you under your New York Medicaid coverage. Medications on the PDL are generally covered without any additional steps, making the process simpler. However, understanding the implications of a drug *not* being on the PDL is equally important.
### Preferred vs. Non-Preferred Drugs
The primary distinction lies between preferred and non-preferred drugs. Preferred drugs are listed on the PDL and are generally covered without prior authorization. Non-preferred drugs are not on the PDL and may require prior authorization before Medicaid will cover them. This means your doctor needs to submit a request to Medicaid, justifying why the non-preferred drug is medically necessary for your specific condition. This process can sometimes cause delays in receiving your medication.
### The Prior Authorization Process
The prior authorization (PA) process can seem complex, but it’s designed to ensure that non-preferred drugs are used appropriately. Here’s a breakdown of the typical steps:
1. **Prescription:** Your doctor prescribes a medication that is not on the PDL.
2. **PA Request:** Your doctor submits a prior authorization request to Medicaid, providing documentation to support the medical necessity of the drug.
3. **Review:** Medicaid reviews the PA request, considering the clinical information provided by your doctor.
4. **Decision:** Medicaid approves or denies the PA request. If approved, the medication is covered. If denied, you may need to consider an alternative medication or appeal the decision.
### Appealing a Prior Authorization Denial
If your prior authorization request is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process typically involves submitting additional information or documentation to support your case. You may also be able to request a hearing to present your case in person.
It’s important to work closely with your doctor and pharmacist throughout the PA and appeals process. They can provide valuable assistance and guidance to help you navigate the system effectively.
## Finding Information on the New York Medicaid PDL
Accessing and understanding the New York Medicaid PDL is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. The PDL is a dynamic document, so it’s important to ensure you are consulting the most up-to-date version. Fortunately, several resources are available to help you find the information you need.
### Official New York Medicaid Website
The official New York Medicaid website is the primary source for accessing the PDL. The website provides a searchable database of preferred drugs, as well as information about the PDL program and prior authorization requirements. You can typically find the PDL document in PDF format for download.
### Searchable Databases and Online Tools
In addition to the official website, several third-party websites and online tools may offer searchable databases of the PDL. These tools can make it easier to find information about specific drugs and their coverage status. However, it’s important to verify the accuracy of any information you find on third-party websites by cross-referencing it with the official New York Medicaid website.
### Consulting Your Doctor or Pharmacist
Your doctor and pharmacist are valuable resources for information about the PDL. They can help you understand the coverage status of your medications and provide guidance on alternative treatment options if necessary. They can also assist with the prior authorization process if you need a non-preferred drug.
## Strategies for Managing Medications Under the PDL
Navigating the New York Medicaid PDL can be made easier with proactive strategies. These strategies focus on communication, understanding your options, and working collaboratively with your healthcare team.
### Communicating with Your Doctor
Open communication with your doctor is essential for managing your medications under the PDL. Be sure to discuss your medication needs and preferences with your doctor, and ask about the coverage status of your drugs. If a medication you need is not on the PDL, work with your doctor to explore alternative options or initiate the prior authorization process.
### Exploring Generic Alternatives
Generic drugs are typically preferred on the PDL due to their lower cost. Discuss with your doctor whether generic alternatives are available for your medications. Generic drugs contain the same active ingredients as brand-name drugs and are generally just as effective and safe.
### Understanding Therapeutic Interchange
Therapeutic interchange refers to the practice of substituting one drug for another that is in the same therapeutic class. The PDL often encourages therapeutic interchange to promote the use of cost-effective medications. Talk to your doctor about whether therapeutic interchange is appropriate for your condition.
## Potential Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the New York Medicaid PDL aims to provide access to affordable medications, challenges can arise. Understanding these potential roadblocks and how to navigate them is crucial for a smooth healthcare experience.
### Limited Access to Certain Medications
One potential challenge is limited access to certain medications that are not on the PDL. This can be particularly problematic for patients who require specific drugs that are not easily substituted. In such cases, it’s important to work closely with your doctor to explore all available options, including prior authorization and appeals.
### Delays in Prior Authorization
Delays in the prior authorization process can also be a challenge. These delays can occur due to administrative issues, incomplete paperwork, or the need for additional clinical information. To minimize delays, ensure that all required documentation is submitted accurately and promptly. Follow up with Medicaid or your doctor’s office to check on the status of your PA request.
### Formulary Changes
The PDL is subject to change, and medications may be added or removed from the list periodically. These changes can be disruptive for patients who are already taking a medication that is no longer preferred. Stay informed about formulary changes by checking the New York Medicaid website regularly or consulting your doctor or pharmacist. Be prepared to discuss alternative treatment options if your medication is affected by a formulary change.
## New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List and Mental Health Medications
It’s worth specifically addressing the nuances of mental health medications and how they interact with the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List. Mental health treatment often requires very specific medications tailored to individual needs, and changes can be disruptive and detrimental. Therefore, understanding the PDL’s impact on these medications is crucial.
### Specific Considerations for Mental Health Medications
Due to the sensitive nature of mental health treatment, alterations to medication regimens need careful consideration. The PDL recognizes this to some extent, but it’s still essential to be proactive.
### Navigating Prior Authorizations for Mental Health Drugs
If a necessary mental health medication is not on the PDL, the prior authorization process becomes even more critical. Ensure your doctor provides comprehensive documentation detailing the patient’s history, the reasons for choosing that specific medication, and potential risks of switching medications. Strong justification significantly increases the likelihood of approval.
### Advocating for Your Mental Health Needs
Don’t hesitate to advocate for your mental health needs. If a prior authorization is denied, explore all available appeals processes. Enlist the support of your doctor, therapist, and any relevant advocacy organizations to strengthen your case. Remember, consistency and stability are paramount in mental health treatment.
## Expert Review of the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List
The New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List is a tool designed to manage costs while ensuring access to necessary medications. While it achieves these goals to some extent, it’s not without its limitations. Our expert review will delve into the pros and cons, offering a balanced perspective.
### User Experience & Usability
The New York Medicaid website is the primary source for accessing the PDL. While the information is available, navigating the website can be challenging. The PDL document itself is often a lengthy PDF, making it difficult to quickly find information on specific drugs. Search functionality could be improved to enhance user experience.
### Performance & Effectiveness
The PDL effectively promotes the use of cost-effective medications, resulting in significant savings for the state. However, the prior authorization process can create delays and administrative burdens for both patients and healthcare providers. The effectiveness of the PDL depends on how well the PA process is managed.
### Pros:
1. **Cost Savings:** The PDL helps control healthcare costs by encouraging the use of generic and preferred drugs.
2. **Access to Medications:** It ensures that Medicaid recipients have access to a wide range of prescription medications.
3. **Therapeutic Alternatives:** It promotes the use of clinically equivalent drugs, providing options for patients and healthcare providers.
4. **Regular Updates:** The PDL is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the latest medical evidence.
5. **Transparency:** The PDL is publicly available, allowing patients and healthcare providers to access information about drug coverage.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Limited Access to Non-Preferred Drugs:** Access to certain medications may be restricted due to prior authorization requirements.
2. **Delays in Prior Authorization:** The PA process can be time-consuming and create delays in medication access.
3. **Formulary Changes:** Changes to the PDL can be disruptive for patients who are already taking a medication.
4. **Administrative Burden:** The PA process can create administrative burdens for healthcare providers.
### Ideal User Profile
The PDL is best suited for Medicaid recipients who are willing to work with their healthcare providers to find cost-effective treatment options. Patients who are flexible and open to trying generic or alternative medications may find the PDL easier to navigate. However, patients with complex medical conditions or who require specific medications may face challenges.
### Key Alternatives
One alternative to the PDL is to explore other insurance options, such as private insurance or Medicare. These plans may offer broader coverage and fewer restrictions on medication access. Another alternative is to participate in patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical manufacturers. These programs can provide free or discounted medications to eligible patients.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
The New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List is a valuable tool for managing healthcare costs and ensuring access to medications. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential challenges and limitations. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to navigate the PDL effectively and advocate for their medication needs. While the PDL has room for improvement in terms of user experience and administrative efficiency, it remains a crucial component of the New York Medicaid program.
## Q&A: Your Top Questions About the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List, designed to address common concerns and provide expert insights:
1. **Q: How often is the New York Medicaid PDL updated?**
**A:** The New York Medicaid PDL is typically updated on a regular basis, often quarterly, but this can vary. The updates reflect changes in drug pricing, the introduction of new medications, and recommendations from the Drug Utilization Review (DUR) Board. Always consult the official New York Medicaid website for the most current version.
2. **Q: What happens if a medication I need is removed from the PDL?**
**A:** If a medication you are currently taking is removed from the PDL, you should consult your doctor immediately. They can discuss alternative treatment options that are on the PDL or initiate a prior authorization request for the non-preferred drug if medically necessary. In many cases, there’s a grace period before the change affects existing prescriptions.
3. **Q: Can I appeal a prior authorization denial? What is the process?**
**A:** Yes, you have the right to appeal a prior authorization denial. The appeals process typically involves submitting a written request for reconsideration, along with any additional supporting documentation. If the initial appeal is unsuccessful, you may have the option to request a hearing. Consult the New York Medicaid website or your Medicaid managed care plan for specific instructions on the appeals process.
4. **Q: Are there any exceptions to the prior authorization requirement for non-preferred drugs?**
**A:** In some cases, exceptions may be made to the prior authorization requirement for non-preferred drugs. These exceptions are typically based on medical necessity and may require documentation from your doctor. Certain emergency situations might also warrant immediate coverage of a non-preferred drug. Check with your doctor or pharmacist for specific details.
5. **Q: How does the PDL affect access to specialty medications?**
**A:** Specialty medications, which are often high-cost and require special handling, may have specific requirements under the PDL. These requirements may include prior authorization, step therapy (trying other medications first), or enrollment in a specialized pharmacy program. Consult the PDL and your Medicaid plan for details on specific specialty medications.
6. **Q: Does the PDL apply to over-the-counter (OTC) medications?**
**A:** Generally, the PDL primarily focuses on prescription medications. However, some OTC medications may be covered under certain circumstances with a prescription from your doctor. Check with your Medicaid plan to determine which OTC medications are covered and what requirements apply.
7. **Q: How can I find out if a specific drug is on the PDL?**
**A:** The easiest way to find out if a specific drug is on the PDL is to use the searchable database on the official New York Medicaid website. You can also ask your doctor or pharmacist to check the PDL for you. Be sure to provide the drug name, dosage, and form (e.g., tablet, capsule, liquid) for accurate results.
8. **Q: What is “step therapy,” and how does it relate to the PDL?**
**A:** Step therapy is a practice that requires patients to try one or more preferred drugs before a non-preferred drug is covered. This is often used for certain conditions where there are multiple treatment options available. The PDL may require step therapy for some medications to encourage the use of cost-effective alternatives.
9. **Q: If I have both Medicare and Medicaid, how does the PDL affect my prescription coverage?**
**A:** If you have both Medicare and Medicaid (dual eligibility), Medicare typically pays for your prescription drugs first. However, Medicaid may cover some drugs that are not covered by Medicare. Consult your Medicare and Medicaid plans for specific details on how your prescription coverage works.
10. **Q: Are there any patient assistance programs available to help with the cost of medications not covered by Medicaid?**
**A:** Yes, many pharmaceutical companies offer patient assistance programs (PAPs) to help eligible patients afford their medications. These programs can provide free or discounted drugs to individuals who meet certain income and medical criteria. Your doctor or pharmacist can help you identify and apply for PAPs that may be available for your medications.
## Conclusion: Navigating the New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List for Optimal Healthcare
The New York Medicaid Preferred Drug List is a critical component of the state’s healthcare system, designed to balance cost-effectiveness with patient access to necessary medications. By understanding the PDL, its principles, and its impact on your medication options, you can proactively manage your healthcare and ensure you receive the treatments you need.
This comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge to navigate the PDL effectively. Remember to communicate openly with your doctor, explore generic alternatives, and understand the prior authorization process. By staying informed and advocating for your health, you can make the most of your New York Medicaid benefits.
Now, we encourage you to take the next step in understanding your healthcare. Visit the official New York Medicaid website to review the latest Preferred Drug List and discuss your medication options with your healthcare provider. Share your experiences with navigating the PDL in the comments below – your insights can help others in the community!
