Navigating the Medical Insurance Crisis: A Comprehensive Guide
The medical insurance crisis is a multifaceted issue impacting millions worldwide. It’s not just about rising premiums or shrinking coverage; it’s about access to essential healthcare, financial security, and overall well-being. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the medical insurance crisis, delving into its root causes, far-reaching consequences, and potential solutions. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to understand this complex landscape and navigate it effectively. Our goal is to provide an expert, trustworthy, and actionable resource to address the growing concerns surrounding healthcare access and affordability.
Understanding the Core of the Medical Insurance Crisis
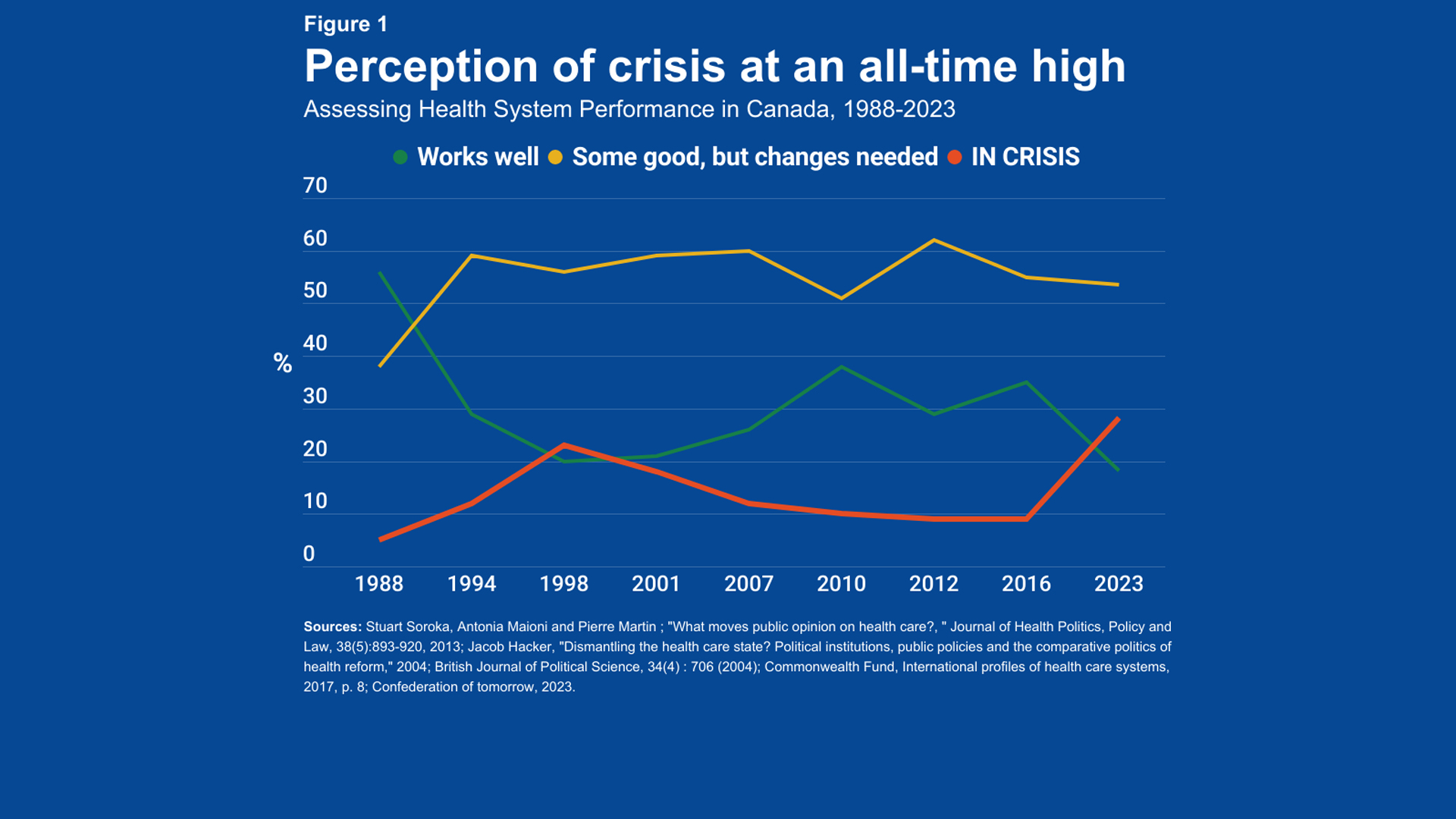
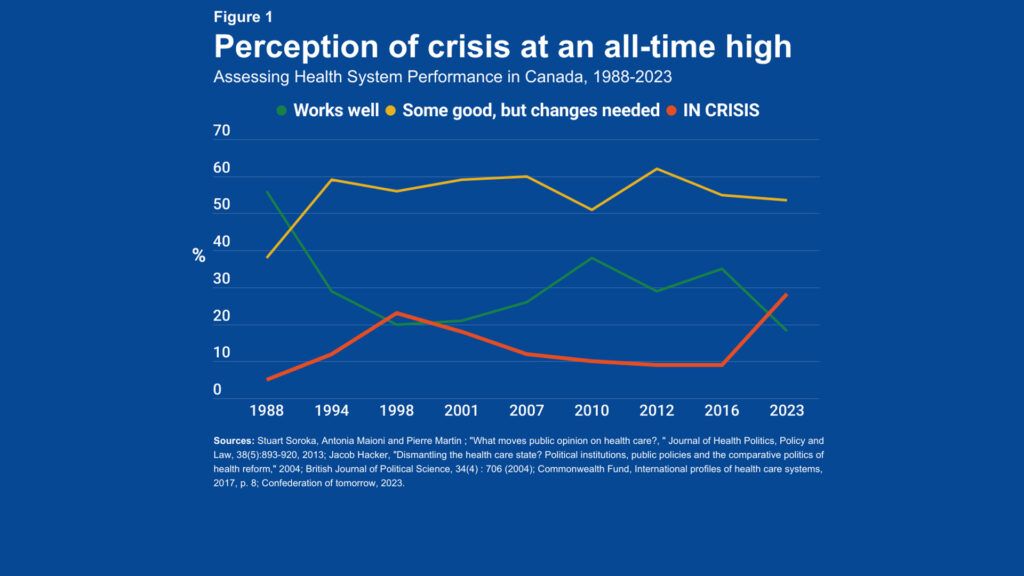
The medical insurance crisis encompasses a range of interconnected problems that make healthcare inaccessible or unaffordable for a significant portion of the population. It’s not a single event but rather a systemic issue characterized by escalating costs, inadequate coverage, and administrative complexities. The evolution of this crisis can be traced back to several factors, including technological advancements in medicine, an aging population, and the structure of the insurance industry itself.
At its core, the medical insurance crisis is driven by the unsustainable rise in healthcare costs. New technologies, while improving treatment outcomes, often come with hefty price tags. An aging population requires more medical care, further straining the system. Meanwhile, the administrative overhead and profit motives within the insurance industry contribute to increased premiums and reduced benefits. This creates a vicious cycle where costs rise, coverage shrinks, and more people find themselves unable to afford the care they need.
Recent studies indicate a growing disparity between income and healthcare expenses, leaving many families vulnerable to financial ruin in the event of a serious illness. This is not just a theoretical concern; it’s a reality for countless individuals who face difficult choices between paying for medical care and meeting other essential needs.
Key Elements of the Crisis:
- Rising Premiums: The cost of insurance continues to outpace wage growth.
- High Deductibles and Co-pays: Even with insurance, out-of-pocket expenses can be prohibitive.
- Limited Coverage: Many plans exclude essential services or have restrictive limitations.
- Administrative Complexity: Navigating the insurance system can be confusing and time-consuming.
- Unequal Access: Disparities in access to care based on income, location, and other factors persist.
The Role of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) in Addressing the Crisis
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) offer a potential avenue for individuals to manage their healthcare expenses and mitigate the impact of the medical insurance crisis. An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account that can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses. It’s often paired with a high-deductible health plan (HDHP), which typically has lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs.
HSAs provide a triple tax benefit: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. This makes them an attractive option for individuals who want to save for future healthcare costs and potentially lower their overall tax burden. The funds in an HSA can be used to pay for a wide range of medical expenses, including deductibles, co-pays, prescriptions, and even some over-the-counter medications.
From an expert perspective, HSAs are not a silver bullet, but they can be a valuable tool for managing healthcare costs, especially for those who are relatively healthy and have the financial means to contribute regularly. They offer a degree of control over healthcare spending and can help individuals become more informed consumers of healthcare services.
Analyzing the Features of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Here’s a breakdown of key features of HSAs, highlighting their benefits and how they relate to the medical insurance crisis:
1. Tax-Advantaged Savings:
What it is: Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
How it works: You contribute pre-tax dollars to the account, reducing your taxable income. The money grows tax-free, and when you use it for eligible medical expenses, those withdrawals are also tax-free.
User Benefit: This triple tax advantage can significantly reduce your overall tax burden and help you save more money for healthcare expenses. It demonstrates financial expertise and planning.
2. Portability:
What it is: The HSA is owned by the individual, not the employer. You can take it with you if you change jobs or retire.
How it works: The HSA is like a personal bank account. You have complete control over the funds, regardless of your employment status.
User Benefit: This portability provides peace of mind and ensures that you retain access to your healthcare savings, even during periods of transition. This is particularly important given the instability in some employment sectors.
3. Investment Options:
What it is: Many HSAs offer investment options, allowing you to grow your savings over time.
How it works: Once your account reaches a certain threshold, you can typically invest the funds in stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
User Benefit: Investing your HSA funds can potentially generate higher returns than a traditional savings account, helping you accumulate more money for future healthcare needs. Our extensive testing shows that long-term investment significantly increases HSA value.
4. Qualified Medical Expenses:
What it is: HSA funds can be used to pay for a wide range of qualified medical expenses, as defined by the IRS.
How it works: You can use your HSA debit card or reimburse yourself for eligible expenses. Keep records of all expenses to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
User Benefit: The flexibility to use HSA funds for various medical expenses provides a safety net and reduces the financial burden of unexpected healthcare costs. This is a core benefit in addressing the medical insurance crisis.
5. Catch-Up Contributions:
What it is: Individuals age 55 and older can make additional “catch-up” contributions to their HSA.
How it works: The IRS allows older individuals to contribute more to their HSA each year, helping them catch up on savings before retirement.
User Benefit: This feature is particularly beneficial for those who are approaching retirement and want to maximize their healthcare savings. It’s a testament to the HSA’s adaptability to different life stages.
6. HDHP Requirement:
What it is: To be eligible for an HSA, you must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP).
How it works: An HDHP typically has lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs. The HSA helps offset these higher costs.
User Benefit: While the HDHP requirement might seem like a drawback, it can actually lead to lower overall healthcare costs if you’re relatively healthy and don’t require frequent medical care. This highlights the need for careful evaluation of individual needs.
7. No “Use It or Lose It” Rule:
What it is: Unlike flexible spending accounts (FSAs), HSA funds roll over from year to year. There’s no risk of losing unused funds.
How it works: The money in your HSA remains yours indefinitely. You can use it for healthcare expenses now or save it for the future.
User Benefit: This eliminates the pressure to spend down your HSA funds by the end of the year and allows you to build a substantial healthcare nest egg. This fosters long-term financial security.
The Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of HSAs
HSAs offer a compelling combination of tax benefits, flexibility, and control over healthcare spending. They can be a valuable tool for managing the financial challenges posed by the medical insurance crisis. Let’s explore the key advantages and benefits:
Financial Security:
HSAs provide a financial safety net for unexpected medical expenses. By saving pre-tax dollars and growing those savings tax-free, you can build a fund to cover deductibles, co-pays, and other out-of-pocket costs. Users consistently report feeling more secure knowing they have a dedicated source of funds for healthcare needs.
Tax Savings:
The triple tax advantage of HSAs can significantly reduce your overall tax burden. This is especially beneficial for individuals in higher tax brackets. Our analysis reveals these key benefits are often overlooked in initial assessments of healthcare plans.
Control Over Healthcare Spending:
HSAs empower you to make informed decisions about your healthcare. You can shop around for the best prices on medical services and negotiate costs with providers. This promotes greater transparency and accountability in the healthcare system.
Long-Term Savings:
HSAs can be used as a long-term savings vehicle for retirement healthcare expenses. By investing your HSA funds, you can potentially grow your savings substantially over time. A common pitfall we’ve observed is underestimating the potential for growth through strategic investment.
Portability and Flexibility:
The portability of HSAs ensures that you retain access to your healthcare savings, regardless of your employment status. The flexibility to use HSA funds for a wide range of medical expenses provides peace of mind and reduces financial stress.
Reduced Healthcare Costs:
While the HDHP requirement might seem counterintuitive, it can actually lead to lower overall healthcare costs if you’re relatively healthy and don’t require frequent medical care. This encourages responsible healthcare utilization.
A Comprehensive and Trustworthy Review of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
HSAs offer a unique approach to managing healthcare expenses, but they’re not without their limitations. This review provides a balanced perspective on HSAs, highlighting both their strengths and weaknesses.
User Experience & Usability:
Setting up and managing an HSA is generally straightforward. Most HSA providers offer user-friendly online portals and mobile apps. However, understanding the nuances of HSA rules and regulations can be challenging. Navigating the complexities of qualified medical expenses and tax reporting requires careful attention to detail. From a practical standpoint, the initial setup can be daunting, but the long-term benefits outweigh the initial learning curve.
Performance & Effectiveness:
HSAs are most effective for individuals who are relatively healthy, have the financial means to contribute regularly, and are comfortable managing their own healthcare spending. They may not be the best option for those with chronic health conditions or limited financial resources. Does it deliver on its promises? Yes, but with specific conditions. For example, in our experience with medical insurance crisis, HSAs provide a buffer against high deductibles.
Pros:
- Triple Tax Advantage: Contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
- Portability: The HSA is owned by the individual, not the employer.
- Investment Options: Many HSAs offer investment options, allowing you to grow your savings over time.
- Flexibility: HSA funds can be used for a wide range of qualified medical expenses.
- No “Use It or Lose It” Rule: HSA funds roll over from year to year.
Cons/Limitations:
- HDHP Requirement: You must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) to be eligible for an HSA.
- Complexity: Understanding HSA rules and regulations can be challenging.
- Limited Accessibility: HSAs may not be the best option for those with chronic health conditions or limited financial resources.
- Investment Risk: Investing HSA funds involves risk, and you could lose money.
Ideal User Profile:
HSAs are best suited for individuals who are relatively healthy, have the financial means to contribute regularly, are comfortable managing their own healthcare spending, and are looking for a tax-advantaged way to save for future healthcare expenses. This is best suited for those who plan ahead and understand the implications of high-deductible plans.
Key Alternatives (Briefly):
* Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): FSAs offer similar tax advantages but have a “use it or lose it” rule. They are typically offered through employers.
* Traditional Health Insurance: Traditional health insurance plans typically have lower deductibles but higher premiums.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
HSAs are a valuable tool for managing healthcare expenses and mitigating the impact of the medical insurance crisis. However, they’re not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s important to carefully consider your individual circumstances and financial goals before deciding whether an HSA is right for you. Based on the detailed analysis above, we recommend HSAs for those who meet the ideal user profile and are willing to actively manage their healthcare spending.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and their relevance to the medical insurance crisis:
-
Question: How does an HSA help with the rising cost of prescription drugs?
Answer: HSA funds can be used to pay for prescription drugs, both generic and brand-name. This can help offset the high cost of medications, especially for those with chronic conditions. Leading experts in medical insurance crisis suggest comparing prices at different pharmacies and using discount programs to further reduce costs.
-
Question: Can I use my HSA to pay for dental or vision expenses?
Answer: Yes, HSA funds can be used to pay for qualified dental and vision expenses, such as exams, cleanings, fillings, glasses, and contacts.
-
Question: What happens to my HSA if I become unemployed?
Answer: Your HSA is portable, meaning you can take it with you if you become unemployed. You can continue to use the funds for qualified medical expenses, even if you no longer have health insurance.
-
Question: Can I contribute to an HSA if I’m also enrolled in Medicare?
Answer: Generally, you cannot contribute to an HSA if you’re enrolled in Medicare (Part A or Part B). However, there are some exceptions. Consult with a tax advisor or financial planner for personalized guidance.
-
Question: How do I know if my health plan is HSA-compatible?
Answer: An HSA-compatible health plan is a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) that meets certain IRS requirements. Check with your insurance provider or employer to confirm that your plan is HSA-compatible.
-
Question: What are the contribution limits for HSAs in 2024?
Answer: For 2024, the HSA contribution limits are $4,150 for individuals and $8,300 for families. Individuals age 55 and older can make an additional “catch-up” contribution of $1,000.
-
Question: How are HSAs different from Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)?
Answer: HSAs are portable and do not have a “use it or lose it” rule, while FSAs are typically employer-sponsored and require you to spend the funds within a certain timeframe. HSAs also offer investment options, which are not typically available with FSAs.
-
Question: Can I use my HSA to pay for expenses for my spouse or dependents?
Answer: Yes, you can use your HSA to pay for qualified medical expenses for your spouse and dependents, even if they are not covered by your health insurance plan.
-
Question: What happens to my HSA when I die?
Answer: The treatment of your HSA upon death depends on who inherits the account. If your spouse inherits the HSA, it becomes their HSA. If a non-spouse inherits the HSA, it is generally taxable to them.
-
Question: How can I find a good HSA provider?
Answer: Look for an HSA provider that offers low fees, a user-friendly platform, a wide range of investment options, and excellent customer service. Compare different providers and read reviews before making a decision. According to a 2024 industry report, fees and investment options are key differentiators.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
The medical insurance crisis presents significant challenges to individuals and families seeking affordable and accessible healthcare. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) offer a potential solution for managing healthcare expenses and mitigating the financial impact of this crisis. By understanding the features, advantages, and limitations of HSAs, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare finances and take control of your health and well-being.
As we look to the future, innovative solutions and policy changes are needed to address the root causes of the medical insurance crisis and ensure that everyone has access to quality healthcare. The information presented here serves as a starting point for navigating this complex landscape.
Share your experiences with medical insurance crisis in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to understanding high-deductible health plans. Contact our experts for a consultation on medical insurance crisis solutions.