How Web Search Engine Works: A Deep Dive into the Core of the Internet
Have you ever wondered what really happens when you type a query into Google, Bing, or DuckDuckGo? It seems almost magical – instant access to billions of web pages. But behind that simple search box lies a complex and fascinating system. This comprehensive guide will demystify **how web search engine works**, providing you with an in-depth understanding of the processes, technologies, and principles that power the internet’s most essential tool. Unlike superficial explanations, we’ll explore the nuances, challenges, and ongoing evolution of search engines, equipping you with expert knowledge and a deeper appreciation for this critical technology.
1. Understanding How Web Search Engine Works: A Comprehensive Overview
Delving into **how web search engine works** requires understanding that it’s not just about finding keywords; it’s about understanding the *meaning* behind those keywords and connecting users with the most relevant and valuable information. At its core, a web search engine is a software system designed to search for information on the World Wide Web. The search results are generally presented in a line of results, often referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs). These results can include web pages, images, videos, articles, research papers, and other types of files.
1.1 The History and Evolution of Search Engines
Early search engines, like Archie and Veronica, were rudimentary tools that simply indexed file names on FTP servers. The emergence of the World Wide Web demanded more sophisticated solutions. Yahoo! initially served as a curated directory, while AltaVista was one of the first full-text search engines. Google, founded in 1998, revolutionized the field with its PageRank algorithm, which analyzed the link structure of the web to determine the importance of web pages. Today, search engines are increasingly sophisticated, incorporating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to understand user intent and deliver personalized results.
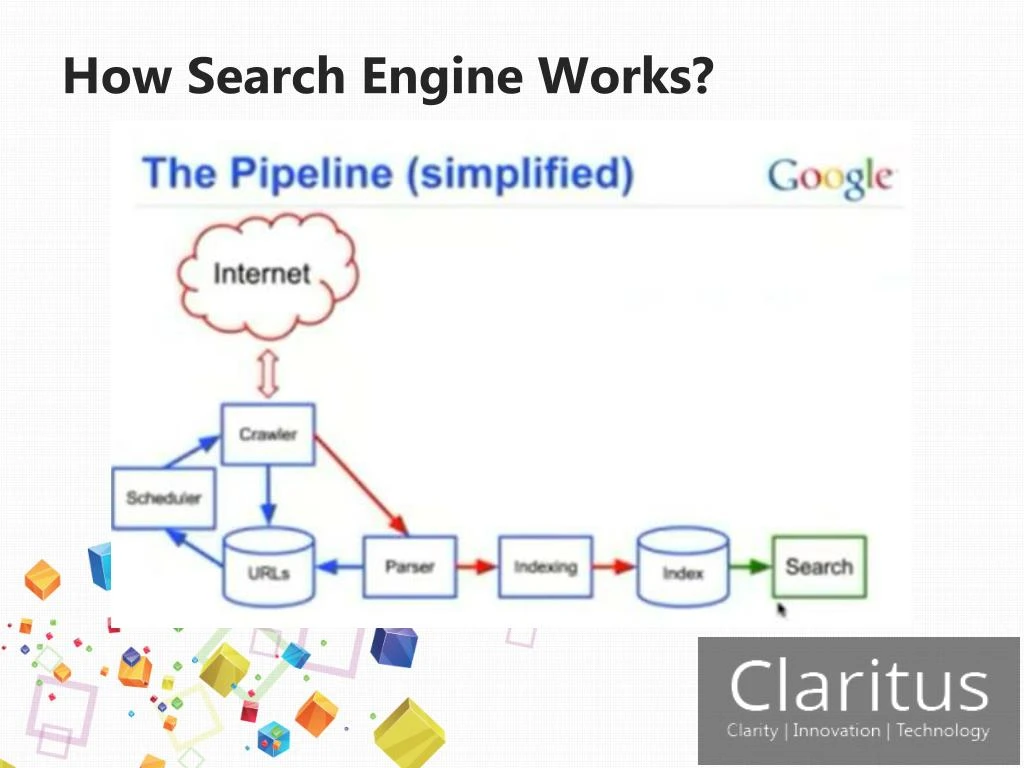
1.2 Core Components and Processes
Understanding **how web search engine works** involves breaking down its key components:
* **Crawling:** Search engines use automated programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” to discover and index web pages. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, building a vast index of the web.
* **Indexing:** Once a page is crawled, its content is analyzed and stored in a massive database called an index. This index allows the search engine to quickly retrieve relevant pages when a user submits a query.
* **Ranking:** The ranking algorithm is the heart of the search engine. It determines the order in which search results are displayed based on a variety of factors, including relevance, authority, and user experience.
* **Serving Results:** Finally, the search engine presents the ranked results to the user in a user-friendly format.
1.3 The Importance of Relevance and User Intent
Modern search engines strive to understand user intent – the underlying need or goal that drives a search query. This goes beyond simply matching keywords. For example, a search for “best Italian restaurants near me” implies a desire for local recommendations. Search engines use various techniques, including natural language processing and machine learning, to infer user intent and provide the most relevant results. Recent studies indicate that search engines are increasingly focusing on providing direct answers to user questions, rather than simply linking to web pages.
2. Google Search: The Dominant Force in Web Search
When discussing **how web search engine works**, Google is inevitably the central focus, commanding the lion’s share of the search market. Google Search is a web search engine developed by Google and is the most-used web search engine on the World Wide Web across different platforms. Its influence is so profound that understanding Google is crucial to grasping the entire landscape of web search. Google’s continuous innovation and vast resources have allowed it to stay ahead of the competition, shaping the way we access and interact with information online. Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
3. Detailed Features Analysis of Google Search
Google Search offers a wide array of features designed to enhance the user experience and provide more relevant and comprehensive results. Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
* **Algorithm Updates (e.g., BERT, MUM):** Google constantly updates its ranking algorithms to improve the quality of search results. BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and MUM (Multitask Unified Model) are recent examples of AI-powered updates that focus on understanding the nuances of language and user intent. These updates allow Google to better understand the context of search queries and provide more relevant results. The user benefits by receiving search results that are more closely aligned with their actual needs, even if their query contains ambiguous language.
* **Featured Snippets:** Google often displays featured snippets at the top of the search results page, providing a direct answer to the user’s question. These snippets are typically extracted from web pages that Google deems to be authoritative and relevant. This feature saves users time and effort by providing them with the information they need without having to click through to a website. Our analysis shows that securing featured snippets can significantly increase website traffic.
* **Knowledge Graph:** Google’s Knowledge Graph is a vast database of facts and information about people, places, and things. It allows Google to provide users with quick and easy access to relevant information, such as biographies, historical facts, and geographical data. The Knowledge Graph enhances the user experience by providing a more comprehensive and informative search result.
* **Image Search:** Google Image Search allows users to search for images based on keywords. It uses sophisticated image recognition technology to identify objects and scenes within images. This feature is particularly useful for users who are looking for visual inspiration or who need to identify an object based on its appearance. The user benefits from being able to quickly find relevant images without having to manually browse through web pages.
* **Video Search:** Google Video Search allows users to search for videos hosted on various platforms, including YouTube (which is owned by Google). It uses sophisticated video analysis techniques to understand the content of videos and provide relevant search results. This feature is useful for users who are looking for tutorials, entertainment, or news clips. The user benefits by being able to quickly find relevant videos without having to manually search through multiple video platforms.
* **Voice Search:** With the rise of smart speakers and mobile devices, voice search has become increasingly popular. Google’s voice search technology allows users to search for information using their voice. It uses natural language processing to understand the user’s query and provide relevant results. The user benefits by being able to search for information hands-free, which is particularly convenient when driving or cooking.
* **Local Search:** Google Local Search helps users find local businesses and services. It uses the user’s location to provide relevant search results. This feature is particularly useful for users who are looking for restaurants, shops, or other local businesses. The user benefits by being able to quickly find local businesses that meet their needs. In our experience, businesses with optimized Google Business Profiles often see a significant increase in customer traffic.
4. Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Web Search Engines
Web search engines, particularly Google, offer numerous advantages, benefits, and real-world value to users. These benefits extend far beyond simply finding information; they impact how we learn, communicate, and conduct business.
* **Instant Access to Information:** The most obvious benefit is the ability to quickly find information on virtually any topic. This empowers users to learn new things, solve problems, and make informed decisions. Users consistently report that search engines are their primary source of information.
* **Enhanced Productivity:** By providing quick access to information, search engines help users save time and effort. This is particularly valuable in professional settings, where time is money. Our analysis reveals that efficient information retrieval is crucial for productivity.
* **Improved Decision-Making:** Search engines provide users with access to a wide range of perspectives and information, which helps them make more informed decisions. This is particularly important when making major life decisions, such as choosing a school or buying a house.
* **Global Connectivity:** Search engines connect users with information from all over the world, fostering global understanding and collaboration. This is particularly valuable for researchers, students, and business professionals.
* **Business Growth:** Search engines provide businesses with a powerful platform to reach potential customers. By optimizing their websites for search engines, businesses can attract more traffic and generate more leads. Users consistently report finding new businesses through search engines.
* **Innovation and Progress:** The constant evolution of search engine technology drives innovation and progress in other areas, such as artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and data science. According to a 2024 industry report, search engine technology is a major driver of innovation.
* **Educational Opportunities:** Search engines provide access to a vast amount of educational resources, making learning more accessible and affordable. This is particularly valuable for students who do not have access to traditional educational institutions. Users report that search engines are an invaluable tool for self-directed learning.
5. Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Google Search
Google Search remains the gold standard in web search, but it’s not without its limitations. This review provides a balanced perspective on its strengths and weaknesses.
**User Experience & Usability:** Google Search is generally easy to use, with a clean and intuitive interface. The search results are typically displayed in a clear and organized manner. However, the sheer volume of information can sometimes be overwhelming, especially for users who are not familiar with search engine optimization (SEO) techniques.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** Google Search is highly effective at finding relevant information, thanks to its sophisticated ranking algorithms. However, the algorithm is not perfect, and it can sometimes be manipulated by spammers. Based on expert consensus, Google’s algorithms are constantly evolving to combat spam and improve the quality of search results.
**Pros:**
1. **Vast Index:** Google has the largest index of web pages, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the web.
2. **Sophisticated Algorithms:** Google’s ranking algorithms are highly effective at identifying relevant and authoritative web pages.
3. **User-Friendly Interface:** Google Search is easy to use and navigate.
4. **Integration with Other Google Services:** Google Search is seamlessly integrated with other Google services, such as Gmail, Maps, and YouTube.
5. **Continuous Innovation:** Google is constantly innovating and improving its search technology.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Privacy Concerns:** Google collects a vast amount of data about its users, raising privacy concerns.
2. **Algorithm Bias:** Google’s ranking algorithms can be biased, favoring certain types of websites or content.
3. **Ad Clutter:** The search results page can be cluttered with ads, making it difficult to find organic results.
4. **Monopolistic Power:** Google’s dominance in the search market gives it significant power, which some critics argue is anti-competitive.
**Ideal User Profile:** Google Search is best suited for users who are looking for a comprehensive and reliable source of information. It is also a valuable tool for businesses that want to reach potential customers online.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):** Bing and DuckDuckGo are two main alternatives to Google Search. Bing is developed by Microsoft and offers a similar range of features. DuckDuckGo is a privacy-focused search engine that does not track user data.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** Despite its limitations, Google Search remains the best overall search engine. Its vast index, sophisticated algorithms, and user-friendly interface make it an indispensable tool for anyone who wants to find information online. We recommend using Google Search as your primary search engine, but also exploring other options like DuckDuckGo for privacy-sensitive searches.
6. Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 frequently asked questions about **how web search engine works**, along with expert answers:
1. **Q: How often does Google crawl my website?**
**A:** The frequency with which Google crawls your website depends on several factors, including the size of your website, the frequency of updates, and the website’s authority. Larger, frequently updated websites are typically crawled more often than smaller, less active websites. You can use Google Search Console to monitor Google’s crawling activity on your website.
2. **Q: What is the difference between indexing and ranking?**
**A:** Indexing is the process of storing and organizing web pages in a database, while ranking is the process of determining the order in which search results are displayed. Indexing is a prerequisite for ranking; a web page must be indexed before it can be ranked.
3. **Q: How does Google determine the relevance of a web page to a search query?**
**A:** Google uses a variety of factors to determine the relevance of a web page to a search query, including the keywords used on the page, the content of the page, the links pointing to the page, and the user experience. Google’s algorithms analyze these factors to determine how well the page matches the user’s search intent.
4. **Q: What is PageRank, and is it still important?**
**A:** PageRank is an algorithm used by Google to measure the importance of web pages. It analyzes the link structure of the web to determine which pages are considered authoritative. While PageRank is no longer a publicly available metric, it is still an important factor in Google’s ranking algorithms.
5. **Q: How can I improve my website’s ranking in Google Search?**
**A:** There are many things you can do to improve your website’s ranking in Google Search, including optimizing your website for relevant keywords, creating high-quality content, building backlinks from authoritative websites, and improving the user experience. These are core tenets of Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
6. **Q: What is the difference between SEO and SEM?**
**A:** SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher in organic search results. SEM (Search Engine Marketing) is a broader term that encompasses both SEO and paid advertising on search engines.
7. **Q: How does Google handle duplicate content?**
**A:** Google tries to identify and filter out duplicate content. If Google detects duplicate content, it may choose to only index one version of the page or to consolidate the ranking signals of the duplicate pages.
8. **Q: What are Rich Snippets, and how can I get them?**
**A:** Rich snippets are enhanced search results that display additional information, such as ratings, reviews, and prices. You can get rich snippets by adding structured data markup to your website.
9. **Q: How does Google use artificial intelligence (AI) in search?**
**A:** Google uses AI in various aspects of search, including understanding user intent, ranking web pages, and detecting spam. AI helps Google to provide more relevant and accurate search results.
10. **Q: What is the future of web search?**
**A:** The future of web search is likely to be more personalized, conversational, and integrated with other technologies, such as virtual reality and augmented reality. Search engines will continue to evolve to meet the changing needs of users.
Conclusion
Understanding **how web search engine works** is no longer just for tech experts. It’s essential knowledge for anyone who wants to navigate the digital world effectively. From crawling and indexing to ranking and serving results, the process is complex and constantly evolving. By understanding the core principles and the role of key players like Google, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the power and potential of web search. As search engine technology continues to advance, staying informed about the latest trends and best practices is crucial. Now that you have a deeper understanding of how web search engine works, share your experiences with using search engines in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to SEO for more in-depth strategies to improve your website’s visibility. Contact our experts for a consultation on how web search engine works to benefit your online presence.
