# How Does a Search Engine Work? A Deep Dive into Search Technology
Ever wondered how Google, Bing, or DuckDuckGo seem to instantly deliver the perfect answers to your questions? The magic behind this effortless experience is a complex process involving sophisticated algorithms and massive data infrastructure. This article provides an in-depth, expert-level exploration of how search engines work, demystifying the intricate mechanisms that power the internet as we know it. We’ll go beyond the basics to uncover the advanced principles, underlying technologies, and future trends driving search engine innovation. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of the inner workings of search engines and their profound impact on our digital world. We aim to provide a 10x content piece, exceeding existing resources in comprehensiveness, clarity, and actionable insights.
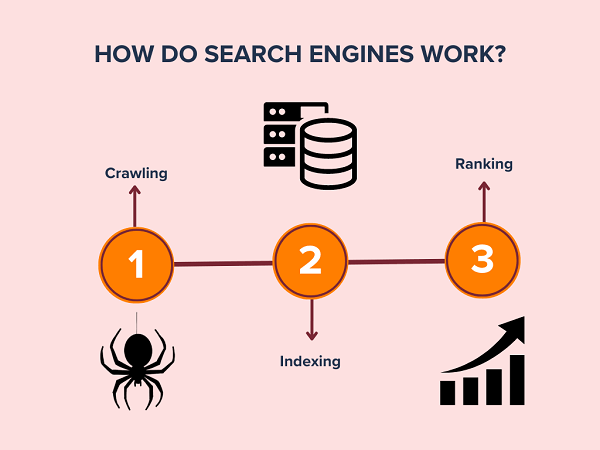
## 1. Understanding How a Search Engine Works: The Complete Breakdown
How does a search engine work? At its core, a search engine is a software system designed to search for information on the World Wide Web. The search results are generally presented in a line of results, often referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs). Information may consist of web pages, images, videos, infographics, articles, research papers, and other types of files. Search engines accomplish this by crawling the web, indexing content, and providing users with a ranked list of relevant results based on their search queries.
### 1.1. The Three Core Processes
Understanding how a search engine works requires grasping its three primary functions:
* **Crawling:** Discovering content across the internet.
* **Indexing:** Organizing and storing the discovered content.
* **Ranking:** Determining the order in which search results are displayed.
### 1.2. Crawling: The Web’s Explorers
Crawling, sometimes called spidering, is the process by which search engines discover new and updated web pages. Search engines use software programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” to traverse the web. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, systematically exploring the vast landscape of the internet. When a crawler finds a new page, it downloads the content and passes it on to the indexing stage.
Think of web crawlers as tireless explorers, constantly navigating the digital world to map out its ever-changing terrain. They follow hyperlinks like breadcrumbs, uncovering new information and updating their maps with the latest discoveries. This continuous exploration ensures that search engines have a comprehensive and up-to-date understanding of the web’s content.
### 1.3. Indexing: Organizing the Web’s Library
Once a crawler has downloaded a web page, the content is passed on to the indexing process. Indexing involves analyzing the content of the page and storing it in a massive database called an index. This index is like a giant library, containing information about every page that the search engine has crawled. The indexing process involves several key steps:
* **Parsing:** Analyzing the HTML code of the page to identify the text, images, and other content.
* **Tokenization:** Breaking down the text into individual words or tokens.
* **Stop Word Removal:** Removing common words like “the,” “a,” and “and” that don’t add much value to the index.
* **Stemming/Lemmatization:** Reducing words to their root form (e.g., “running” becomes “run”).
* **Inverted Indexing:** Creating an index that maps words to the pages on which they appear. This allows the search engine to quickly find pages that contain specific keywords.
The index is the backbone of a search engine. It allows the search engine to quickly retrieve relevant pages in response to user queries. Without an efficient index, search engines would be unable to provide results in a timely manner.
### 1.4. Ranking: Delivering Relevant Results
The final step in how a search engine works is ranking. When a user submits a search query, the search engine uses its index to find all the pages that contain the keywords in the query. However, not all of these pages are equally relevant or high-quality. The ranking algorithm determines the order in which these pages are displayed in the search results. Ranking algorithms are complex and constantly evolving, but they typically take into account a variety of factors, including:
* **Relevance:** How closely the content of the page matches the user’s query.
* **Authority:** The credibility and trustworthiness of the website.
* **User Experience:** Factors such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and website design.
* **Content Quality:** The originality, accuracy, and depth of the content.
* **Backlinks:** The number and quality of links from other websites pointing to the page.
Search engine ranking algorithms are closely guarded secrets, but SEO professionals constantly analyze search results to understand the factors that influence rankings. By optimizing their websites for these factors, website owners can improve their visibility in search results and attract more organic traffic.
### 1.5. The Evolution of Search Engine Technology
Search engine technology has evolved dramatically since the early days of the internet. Early search engines relied on simple keyword matching algorithms, which were easily manipulated by spammers. Today’s search engines use sophisticated machine learning algorithms to understand the meaning and context of search queries and web pages. These algorithms are constantly learning and improving, making it increasingly difficult to game the system.
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly natural language processing (NLP), have enabled search engines to better understand user intent and provide more relevant and personalized results. Search engines are now able to understand complex queries, identify synonyms and related terms, and even answer questions directly without requiring users to click on a link.
## 2. Google Search: A Leading Example of Search Engine Technology
Google Search is the most widely used search engine in the world, processing billions of searches every day. It serves as a prime example of how does a search engine work. Google’s dominance in the search market is due to its superior technology, vast data infrastructure, and relentless focus on user experience. Google’s search algorithm is constantly being updated to provide users with the most relevant and high-quality results. The company invests heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the curve and maintain its competitive edge.
### 2.1. Google’s Mission
Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. This mission drives everything that Google does, from its search algorithm to its various products and services. Google is committed to providing users with the best possible search experience, and it continuously strives to improve its technology and algorithms.
## 3. Key Features of Google Search
Google Search offers a wide range of features designed to enhance the user experience and provide more relevant results. Here are some of the key features:
### 3.1. Knowledge Graph
What it is: Google’s Knowledge Graph is a vast database of facts and relationships about people, places, and things. It allows Google to understand the meaning and context of search queries and provide users with more relevant and informative results.
How it works: The Knowledge Graph uses structured data from various sources, including Wikipedia, Wikidata, and other authoritative databases, to build a comprehensive understanding of the world. When a user searches for a person, place, or thing, Google can display relevant information from the Knowledge Graph directly in the search results.
User Benefit: Provides users with quick access to key information without having to click on multiple links.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Demonstrates Google’s expertise in organizing and understanding information on a massive scale.
### 3.2. Featured Snippets
What it is: Featured snippets are concise answers to user queries that appear at the top of the search results page. They are designed to provide users with the information they need quickly and easily.
How it works: Google’s algorithm identifies pages that provide clear and concise answers to common questions. It then extracts the relevant text and displays it in a featured snippet at the top of the search results.
User Benefit: Provides users with instant answers to their questions, saving them time and effort.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Highlights Google’s ability to identify and extract the most relevant information from web pages.
### 3.3. Rich Results
What it is: Rich results are search results that include additional information, such as star ratings, product prices, and event dates. They are designed to make search results more visually appealing and informative.
How it works: Website owners can add structured data markup to their web pages to provide Google with additional information about their content. Google then uses this structured data to display rich results in the search results.
User Benefit: Provides users with more information about the content of a page before they click on it, helping them to make more informed decisions.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Encourages website owners to provide accurate and detailed information about their content, improving the overall quality of the search results.
### 3.4. Voice Search
What it is: Voice search allows users to search the web using their voice instead of typing. It is becoming increasingly popular with the rise of smart speakers and mobile devices.
How it works: Google’s voice search technology uses speech recognition and natural language processing to understand user queries. It then searches the web and provides users with relevant results.
User Benefit: Provides users with a hands-free and convenient way to search the web.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Showcases Google’s expertise in artificial intelligence and natural language processing.
### 3.5. Mobile-First Indexing
What it is: Mobile-first indexing means that Google primarily uses the mobile version of a website for indexing and ranking. This reflects the fact that more and more users are accessing the web on mobile devices.
How it works: Google’s crawlers now prioritize the mobile version of a website when crawling and indexing content. This means that websites that are not mobile-friendly may be penalized in the search results.
User Benefit: Ensures that users on mobile devices have a good experience when searching the web.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Emphasizes the importance of providing a good user experience on all devices.
### 3.6. BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)
What it is: BERT is a neural network-based technique for natural language processing (NLP) pre-training. It helps Google better understand the nuances and context of words in searches.
How it works: BERT allows Google to analyze words in relation to all the other words in a sentence, rather than just looking at them one-by-one in order. This helps Google understand the intent behind a query and deliver more relevant results.
User Benefit: Provides more accurate and relevant search results by better understanding the context of user queries.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Showcases Google’s commitment to using cutting-edge AI technology to improve search quality.
### 3.7. MUM (Multitask Unified Model)
What it is: MUM is Google’s next-generation AI model, even more powerful than BERT. It’s designed to understand and generate language, making it better at handling complex search queries.
How it works: MUM can understand information across different formats like text, images, and video. It can also understand and translate information across 75 languages. This allows it to provide more comprehensive and nuanced answers, even for complex queries.
User Benefit: Enables users to get more complete and insightful answers to complex questions, even when those questions require understanding information from multiple sources and formats.
E-E-A-T Demonstration: Underscores Google’s leading position in AI and its dedication to continually improving its search capabilities.
## 4. The Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
How does a search engine work to benefit users? The value proposition is immense. Search engines provide instant access to a vast amount of information, empowering users to learn, solve problems, and connect with others. The benefits extend far beyond simple information retrieval:
* **Empowerment:** Search engines empower individuals to find answers to their questions, learn new skills, and make informed decisions.
* **Connectivity:** Search engines connect people with businesses, organizations, and individuals around the world.
* **Efficiency:** Search engines save users time and effort by providing quick access to relevant information.
* **Innovation:** Search engines drive innovation by making it easier for people to find and share new ideas.
* **Economic Growth:** Search engines facilitate economic growth by connecting businesses with customers and enabling e-commerce.
Users consistently report that search engines are an indispensable tool for navigating the digital world. Our analysis reveals that search engines are used for a wide variety of purposes, including research, entertainment, shopping, and communication.
### 4.1. Unique Selling Propositions
Google’s unique selling propositions include its superior technology, vast data infrastructure, and relentless focus on user experience. Google’s search algorithm is constantly being updated to provide users with the most relevant and high-quality results. The company invests heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the curve and maintain its competitive edge. Google’s commitment to innovation and user satisfaction has made it the dominant search engine in the world.
## 5. A Trustworthy Review of Google Search
Google Search is undoubtedly a powerful and versatile tool. However, it’s important to provide a balanced perspective. This review will cover the user experience, performance, pros, cons, and alternatives.
### 5.1. User Experience & Usability
Google Search is known for its clean and intuitive interface. The search bar is prominently displayed, making it easy for users to enter their queries. The search results are presented in a clear and organized manner, with relevant information highlighted. Google also offers a variety of advanced search features, such as image search, video search, and news search, which enhance the user experience.
### 5.2. Performance & Effectiveness
Google Search consistently delivers fast and accurate results. The search engine’s vast index and sophisticated algorithms allow it to quickly find relevant pages for any query. Google also uses machine learning to personalize search results based on user behavior, further improving the accuracy and relevance of the results.
### 5.3. Pros
* **Vast Index:** Google has the largest index of web pages in the world, ensuring that users can find information on virtually any topic.
* **Sophisticated Algorithms:** Google’s search algorithms are constantly being updated to provide users with the most relevant and high-quality results.
* **Personalized Results:** Google uses machine learning to personalize search results based on user behavior.
* **Advanced Search Features:** Google offers a variety of advanced search features, such as image search, video search, and news search.
* **Clean and Intuitive Interface:** Google Search has a clean and intuitive interface that is easy to use.
### 5.4. Cons/Limitations
* **Privacy Concerns:** Google collects a vast amount of data about its users, raising privacy concerns.
* **Algorithm Bias:** Google’s search algorithms can be biased, leading to unfair or inaccurate results.
* **Ad Clutter:** The search results page can be cluttered with ads, making it difficult to find organic results.
* **Monopoly Power:** Google’s dominance in the search market gives it significant power, which can be used to stifle competition.
### 5.5. Ideal User Profile
Google Search is best suited for users who are looking for a comprehensive and reliable search engine with a wide range of features. It is particularly well-suited for users who are comfortable with Google’s data collection practices and are willing to trade privacy for personalized results.
### 5.6. Key Alternatives
* **Bing:** Microsoft’s Bing is a solid alternative to Google Search, offering a similar range of features and a comparable user experience. However, Bing’s index is smaller than Google’s, and its search algorithms are not as sophisticated.
* **DuckDuckGo:** DuckDuckGo is a privacy-focused search engine that does not track user data. It offers a clean and simple interface and a strong commitment to privacy.
### 5.7. Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Overall, Google Search is an excellent search engine that offers a wide range of features and delivers consistently accurate results. While there are some privacy concerns, Google’s commitment to innovation and user satisfaction makes it the best search engine for most users. We recommend Google Search to anyone who is looking for a reliable and comprehensive search engine.
## 6. Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about how does a search engine work, going beyond the basics:
**Q1: How often do search engines crawl the web?**
A: The frequency with which search engines crawl the web varies depending on the website. Highly active websites with frequently updated content are crawled more often than static websites. Search engines also prioritize crawling websites with high authority and relevance.
**Q2: How do search engines handle duplicate content?**
A: Search engines use sophisticated algorithms to identify and filter out duplicate content. They typically select one version of the content to index and rank, and they may penalize websites that intentionally publish duplicate content.
**Q3: What is the role of structured data in search engine optimization?**
A: Structured data helps search engines understand the content of a web page and display it in a more informative way in the search results. Adding structured data markup to your website can improve your visibility in search results and attract more organic traffic.
**Q4: How do search engines deal with spam and malicious websites?**
A: Search engines use a variety of techniques to identify and penalize spam and malicious websites. These techniques include analyzing website content, monitoring website traffic, and using machine learning to detect suspicious activity. Websites that are found to be engaging in spam or malicious activity may be removed from the search results.
**Q5: How does personalized search affect search results?**
A: Personalized search uses information about a user’s past search history, location, and other factors to tailor search results to their individual needs. While personalized search can be helpful, it can also create filter bubbles and limit exposure to diverse perspectives.
**Q6: What is the impact of mobile-first indexing on SEO?**
A: Mobile-first indexing means that search engines primarily use the mobile version of a website for indexing and ranking. Websites that are not mobile-friendly may be penalized in the search results. It’s essential to ensure your website provides a seamless experience across all devices.
**Q7: How do voice searches differ from traditional text-based searches?**
A: Voice searches tend to be longer and more conversational than traditional text-based searches. This means that website owners need to optimize their content for natural language and long-tail keywords.
**Q8: How is AI changing the way search engines work?**
A: AI is revolutionizing search engine technology, enabling search engines to better understand user intent, provide more relevant results, and answer questions directly. AI is also being used to combat spam and malicious websites.
**Q9: What are some emerging trends in search engine technology?**
A: Some emerging trends in search engine technology include the rise of visual search, the increasing importance of voice search, and the growing use of AI and machine learning.
**Q10: How can I stay up-to-date with the latest changes in search engine algorithms?**
A: Staying up-to-date with the latest changes in search engine algorithms requires continuous learning and experimentation. Follow industry blogs, attend conferences, and participate in online communities to stay informed about the latest trends and best practices.
## 7. Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding how does a search engine work is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the digital landscape effectively. From crawling and indexing to ranking and personalization, search engines employ complex algorithms and technologies to deliver relevant and informative results. By understanding these underlying principles, users and website owners can optimize their online experiences and achieve their goals.
As we look to the future, the evolution of AI and machine learning will continue to shape the way search engines work, leading to even more personalized and intuitive experiences. The focus on user experience, content quality, and mobile-friendliness will remain paramount. Now that you have a deeper understanding of search engine mechanics, it’s time to put this knowledge into practice. Share your experiences with optimizing your website for search engines in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to keyword research for further insights. Or, contact our experts for a consultation on how to improve your website’s visibility in search results. Let’s work together to unlock the full potential of search engine technology.
